A basic study design for expedited safety signal evaluation based on electronic healthcare data
- PMID: 20681003
- PMCID: PMC2917262
- DOI: 10.1002/pds.1926
A basic study design for expedited safety signal evaluation based on electronic healthcare data
Abstract
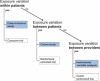
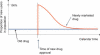
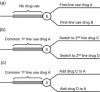
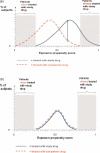
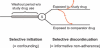
Active drug safety monitoring based on longitudinal electronic healthcare databases (a Sentinel System), as outlined in recent FDA-commissioned reports, consists of several interlocked processes, including signal generation, signal strengthening, and signal evaluation. Once a signal of a potential drug safety issue is generated, signal strengthening and signal evaluation have to follow in short sequence in order to quickly provide as much information about the triggering drug-event association as possible. This paper proposes a basic study design based on the incident user cohort design for expedited signal evaluation in longitudinal healthcare databases. It will not resolve all methodological issues nor will it fit all study questions arising within the framework of a Sentinel System. It should rather be seen as a guidance that will fit the majority of situations and serve as a starting point for adaptations to specific studies. Such an approach will expedite and structure the process of study development and highlight specific assumptions, which is particularly valuable in a Sentinel System where signals are by definition preliminary and evaluation of signals is time critical.
2010 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

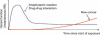


References
-
- Platt R, Wilson M, Chan KA, Benner JS, Marchibroda J, McClellan M. The new Sentinel Network–improving the evidence of medical-product safety. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:645–647. - PubMed
-
- Avorn J, Schneeweiss S. Managing drug-risk information–what to do with all those new numbers. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:647–649. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration FDA's Sentinel Initiative. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/FDAsSentinelInitiative/default.htm.
-
- Walker AM. Orthogonal predictions: follow-up questions for suggestive data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010 in press. - PubMed
-
- Schneeweiss S, Glynn RJ, Tsai EH, Avorn J, Solomon DH. Adjusting for unmeasured confounders in pharmacoepidemiologic claims data using external information: the example of COX2 inhibitors and myocardial infarction. Epidemiology. 2005;16:17–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

