[The correlation between the expression of Wnt1 and prognosis in resected non-small cell lung cancer]
- PMID: 20681444
- PMCID: PMC6015161
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.06.004
[The correlation between the expression of Wnt1 and prognosis in resected non-small cell lung cancer]
Abstract
Background and objective: Wnt1 protein is the first factor in Wnt signaling pathway. It has been proven that high expression of Wnt1 protein was associated with malignant proliferation in many tumors. The aim of this study is to investigate the correlation between Wnt1 protein overexpression, clinicopathologic features and survival in resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining of Envision was applied to investigate the expression of Wnt1 protein in specimens of 115 NSCLC and 19 benign pulmonary diseases. The correlation between the Wnt1 protein in specimens of 115 NSCLC and clinicopathologic features was analysed with chi2 test, and the correlation between the Wnt1 protein expression and the patient survival was evaluated with Kaplan-Meier survival curve and Cox regression.
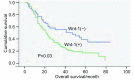
Results: The positive rate ofWnt1 protein in specimens of NSCLC was 62.6%, which was significantly higher than 31.6% of benign pulmonary diseases (chi2 = 4.474, P = 0.034). But it was not correlated with clinicopathologic features. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Log-rank test suggested that patients with Wnt1 protein overexpression had poor prognosis (P = 0.003). And Cox regression suggested Wnt1 protein expression was an independent prognostic factor of NSCLC.
Conclusion: The expression of Wnt1 was remarkably higher in specimens of resected NSCLC than that in benign pulmonary diseases. Overexpression of Wnt1 protein in NSCLC was correlated with prognosis and can be served as an independent prognostic factor of NSCLC.
背景与目的: Wnt1蛋白是Wnt信号传导通路的第一个因子,其高表达与很多肿瘤相关,本研究旨在探讨Wnt1蛋白在非小细胞肺癌组织(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)中的表达及与预后的相关性。
方法: 选取术后经病理证实的115例NSCLC和19例肺良性病变(5例肺结核、4例支气管扩张、6例肺大疱、4例炎性假瘤),运用免疫组化Envision法检测Wnt1蛋白的表达,采用χ2检验分析Wnt1蛋白在NSCLC及良性组织中表达的差异及NSCLC中Wnt1蛋白表达与临床病理特征的相关性。采用Kaplan-Meier生存分析和Cox回归分析方法分析Wnt1蛋白在NSCLC组织中的表达和预后的关系。
结果: Wnt1在NSCLC组织中表达的阳性率为62.6%,显著高于对照组的31.6%(χ2=4.474, P=0.034),但与临床病理特征无相关性。Kaplan-Meier生存分析、Log-rank检验提示Wnt1阳性表达的NSCLC的患者预后较差(P=0.003),Cox回归分析结果表明,Wnt1蛋白是影响NSCLC预后的独立危险因素(OR=1.834, P=0.032)。
结论: Wnt1蛋白在NSCLC组织中的阳性表达率高于肺良性病变组织;Wnt1蛋白阳性表达者预后差,可以作为判断NSCLC预后的参考指标。
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aberrant Wnt1/β-catenin expression is an independent poor prognostic marker of non-small cell lung cancer after surgery.J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Apr;6(4):716-24. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31820c5189. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21336184
-
High expression of the transcriptional co-activator p300 predicts poor survival in resectable non-small cell lung cancers.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012 Jun;38(6):523-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2012.02.180. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22440742
-
Wnt1 overexpression associated with tumor proliferation and a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Oncol Rep. 2008 Jan;19(1):203-9. Oncol Rep. 2008. PMID: 18097596
-
Clinicopathologic features and prognostic implications of Gankyrin protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2015 Dec;211(12):939-47. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Pathol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26554593
-
Phosphorylated Akt overexpression and loss of PTEN expression in non-small cell lung cancer confers poor prognosis.Lung Cancer. 2006 Feb;51(2):181-91. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.10.003. Lung Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16324768
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of wingless-type proteins in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016 Aug;5(4):436-42. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2016.08.08. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27652206 Free PMC article.
-
Emetine Synergizes with Cisplatin to Enhance Anti-Cancer Efficacy against Lung Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 25;20(23):5914. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235914. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31775307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nusse R, Brown A, Papkoff J, et al. A new nomenclature for int-1 and related genes: the wnt gene family. http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/88071/ Cell. 1991;64(2):231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

