In vitro selection of a DNA-templated small-molecule library reveals a class of macrocyclic kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 20681606
- PMCID: PMC2924185
- DOI: 10.1021/ja104903x
In vitro selection of a DNA-templated small-molecule library reveals a class of macrocyclic kinase inhibitors
Abstract
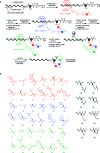
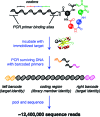
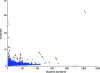
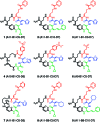
DNA-templated organic synthesis enables the translation of DNA sequences into synthetic small-molecule libraries suitable for in vitro selection. Previously, we described the DNA-templated multistep synthesis of a 13,824-membered small-molecule macrocycle library. Here, we report the discovery of small molecules that modulate the activity of kinase enzymes through the in vitro selection of this DNA-templated small-molecule macrocycle library against 36 biomedically relevant protein targets. DNA encoding selection survivors was amplified by PCR and identified by ultra-high-throughput DNA sequencing. Macrocycles corresponding to DNA sequences enriched upon selection against several protein kinases were synthesized on a multimilligram scale. In vitro assays revealed that these macrocycles inhibit (or activate) the kinases against which they were selected with IC(50) values as low as 680 nM. We characterized in depth a family of macrocycles enriched upon selection against Src kinase, and showed that inhibition was highly dependent on the identity of macrocycle building blocks as well as on backbone conformation. Two macrocycles in this family exhibited unusually strong Src inhibition selectivity even among kinases closely related to Src. One macrocycle was found to activate, rather than inhibit, its target kinase, VEGFR2. Taken together, these results establish the use of DNA-templated synthesis and in vitro selection to discover small molecules that modulate enzyme activities, and also reveal a new scaffold for selective ATP-competitive kinase inhibition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Highly specific, bisubstrate-competitive Src inhibitors from DNA-templated macrocycles.Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Feb 19;8(4):366-74. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.792. Nat Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22344177 Free PMC article.
-
Translation of DNA into a library of 13,000 synthetic small-molecule macrocycles suitable for in vitro selection.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Nov 19;130(46):15611-26. doi: 10.1021/ja805649f. Epub 2008 Oct 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18956864 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Biochemical Basis for Intracellular Kinase Inhibition by Src-specific Peptidic Macrocycles.Cell Chem Biol. 2016 Sep 22;23(9):1103-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.07.017. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Cell Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27593110 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling in Tumor Cells by Small Molecule Src Family Kinase Inhibitors.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(10):1351-1356. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666170103094946. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28044939 Review.
-
Development and strategies of VEGFR-2/KDR inhibitors.Future Med Chem. 2012 Sep;4(14):1839-52. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.121. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23043480 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Cell-Permeable Cyclic Peptidyl Inhibitor against the Keap1-Nrf2 Interaction.J Org Chem. 2020 Feb 7;85(3):1416-1424. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b02367. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Org Chem. 2020. PMID: 31609620 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide-Based Systems for Input-Controlled and Non-Covalently Regulated Protein-Binding.Supramol Chem. 2013 Jan 1;25(12):10.1080/10610278.2013.810337. doi: 10.1080/10610278.2013.810337. Supramol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24187478 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ligand-target pairs from combined libraries of small molecules and unpurified protein targets in cell lysates.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Feb 26;136(8):3264-70. doi: 10.1021/ja412934t. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24495225 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning Protein Surfaces with DNA-Encoded Libraries.ChemMedChem. 2021 Apr 8;16(7):1048-1062. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000869. Epub 2020 Dec 28. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33295694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly specific, bisubstrate-competitive Src inhibitors from DNA-templated macrocycles.Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Feb 19;8(4):366-74. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.792. Nat Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22344177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lam K. S.; Lebl M.; Krchnak V. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 411–448. - PubMed
-
- Pirrung M. C. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 473–488. - PubMed
-
- Tan D. S. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 74–84. - PubMed
-
- Walters W. P.; Namchuk M. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2003, 2, 259–266. - PubMed
-
- Joyce G. F. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 791–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

