Circadian wheel-running activity during withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol exposure in mice
- PMID: 20682191
- PMCID: PMC2916875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2010.02.011
Circadian wheel-running activity during withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol exposure in mice
Abstract
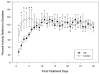
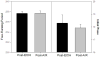
Alcohol withdrawal is associated with affective-behavioral disturbances in both human alcoholics and in animal models. In general, these phenomena are potentiated by increased alcohol exposure duration and by prior withdrawal episodes. Previous studies have also reported locomotor hypoactivity during ethanol withdrawal in rats and mice, but only in novel test environments and not in the home cage. In the present study, we examined the effects of withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) vapor exposure on the level and circadian periodicity of wheel-running activity in C57BL/6J mice. CIE treatment resulted in reductions in wheel-running activity compared with plain-air controls that persisted for about 1 week after withdrawal. Analysis of circadian waveforms indicated that reduced activity occurred throughout the night phase, but that daily-activity patterns were otherwise unaltered. CIE failed to alter free-running circadian period or phase in animals maintained under constant darkness. These results show that ethanol withdrawal can result in locomotor hypoactivity even in the habitual, home-cage environment, and suggest that withdrawal-related reductions in wheel-running activity may reflect the specific motivational significance of this behavior.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


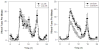
References
-
- Becker HC, Diaz-Granados JL, Weathersby RT. Repeated ethanol withdrawal experience increases the severity and duration of subsequent withdrawal seizures in mice. Alcohol. 1997;14:319–326. - PubMed
-
- Becker HC, Hale RL. Repeated episodes of ethanol withdrawal otentiate the severity of subsequent withdrawal seizures: an animal model of alcohol withdrawal “kindling”. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1993;17:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Becker HC, Lopez MF. Increased ethanol drinking after repeated chronic ethanol exposure and withdrawal experience in C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:1829–1838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

