Cell membrane tethers generate mechanical force in response to electrical stimulation
- PMID: 20682262
- PMCID: PMC3297770
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.05.025
Cell membrane tethers generate mechanical force in response to electrical stimulation
Abstract
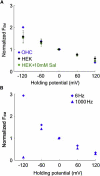
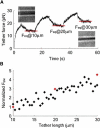
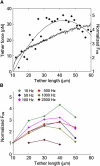
Living cells maintain a huge transmembrane electric field across their membranes. This electric field exerts a force on the membrane because the membrane surfaces are highly charged. We have measured electromechanical force generation by cell membranes using optically trapped beads to detach the plasma membrane from the cytoskeleton and form long thin cylinders (tethers). Hyperpolarizing potentials increased and depolarizing potentials decreased the force required to pull a tether. The membrane tether force in response to sinusoidal voltage signals was a function of holding potential, tether diameter, and tether length. Membrane electromechanical force production can occur at speeds exceeding those of ATP-based protein motors. By harnessing the energy in the transmembrane electric field, cell membranes may contribute to processes as diverse as outer hair cell electromotility, ion channel gating, and transport.
2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
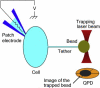
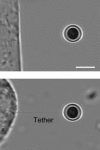
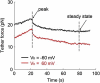
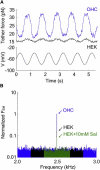
Similar articles
-
Effects of prestin on membrane mechanics and electromechanics.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007;2007:5384-6. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4353559. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007. PMID: 18003225
-
Prestin modulates mechanics and electromechanical force of the plasma membrane.Biophys J. 2007 Jul 1;93(1):L07-9. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.107573. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17468166 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical properties of neuronal growth cone membranes studied by tether formation with laser optical tweezers.Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):988-96. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80274-2. Biophys J. 1995. PMID: 7756561 Free PMC article.
-
Electromechanical models of the outer hair cell composite membrane.J Membr Biol. 2006 Feb-Mar;209(2-3):135-52. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0843-7. Epub 2006 May 25. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16773498 Review.
-
Molecular aspects of electrical excitation in lipid bilayers and cell membranes.Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1976;2:230-84. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1976. PMID: 776770 Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling by neuronal swelling.Sci Signal. 2011 Jan 11;4(155):tr1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.4155tr1. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21224445 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-GUV patch-clamping.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 10;114(2):328-333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609142114. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28003462 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Membrane Tension Gradients, Membrane Flows, and Cellular Processes.Physiology (Bethesda). 2024 Jul 1;39(4):0. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00007.2024. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Physiology (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38501962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A motif of eleven amino acids is a structural adaptation that facilitates motor capability of eutherian prestin.J Cell Sci. 2012 Feb 15;125(Pt 4):1039-47. doi: 10.1242/jcs.097337. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22399806 Free PMC article.
-
Informing the Cannabis Conjecture: From Life's Beginnings to Mitochondria, Membranes and the Electrome-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 22;24(17):13070. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713070. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dowhan W., Bogdanov M., Mileykowskaya E. Functional roles of lipids in membranes. In: Vance D.E., Vance J.E., editors. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes. Elsevier B.V. Dordrecht; The Netherlands: 2008.
-
- Daleke D.L. Regulation of transbilayer plasma membrane phospholipid asymmetry. J. Lipid Res. 2003;44:233–242. - PubMed
-
- Cohen L.B., Keynes R.D., Hille B. Light scattering and birefringence changes during nerve activity. Nature. 1968;218:438–441. - PubMed
-
- Iwasa K., Tasaki I. Mechanical changes in squid giant axons associated with production of action potentials. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980;95:1328–1331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

