Computing moment-to-moment BOLD activation for real-time neurofeedback
- PMID: 20682350
- PMCID: PMC3731777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.060
Computing moment-to-moment BOLD activation for real-time neurofeedback
Abstract
Estimating moment-to-moment changes in blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) activation levels from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data has applications for learned regulation of regional activation, brain state monitoring, and brain-machine interfaces. In each of these contexts, accurate estimation of the BOLD signal in as little time as possible is desired. This is a challenging problem due to the low signal-to-noise ratio of fMRI data. Previous methods for real-time fMRI analysis have either sacrificed the ability to compute moment-to-moment activation changes by averaging several acquisitions into a single activation estimate or have sacrificed accuracy by failing to account for prominent sources of noise in the fMRI signal. Here we present a new method for computing the amount of activation present in a single fMRI acquisition that separates moment-to-moment changes in the fMRI signal intensity attributable to neural sources from those due to noise, resulting in a feedback signal more reflective of neural activation. This method computes an incremental general linear model fit to the fMRI time series, which is used to calculate the expected signal intensity at each new acquisition. The difference between the measured intensity and the expected intensity is scaled by the variance of the estimator in order to transform this residual difference into a statistic. Both synthetic and real data were used to validate this method and compare it to the only other published real-time fMRI method.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
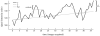
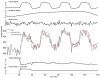
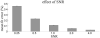
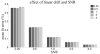
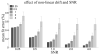
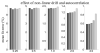
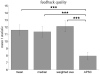
Similar articles
-
Real-time and Recursive Estimators for Functional MRI Quality Assessment.Neuroinformatics. 2022 Oct;20(4):897-917. doi: 10.1007/s12021-022-09582-7. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Neuroinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35297018
-
When the Brain Takes 'BOLD' Steps: Real-Time fMRI Neurofeedback Can Further Enhance the Ability to Gradually Self-regulate Regional Brain Activation.Neuroscience. 2018 May 15;378:71-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.09.026. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 27659118 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological self-regulation of regional brain activity using real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI): methodology and exemplary data.Neuroimage. 2003 Jul;19(3):577-86. doi: 10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00145-9. Neuroimage. 2003. PMID: 12880789 Clinical Trial.
-
Self-regulation of local brain activity using real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI).J Physiol Paris. 2004 Jul-Nov;98(4-6):357-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2005.09.019. Epub 2005 Nov 10. J Physiol Paris. 2004. PMID: 16289548 Review.
-
Pitfalls in FMRI.Eur Radiol. 2009 Nov;19(11):2689-706. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1456-9. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Eur Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19504107 Review.
Cited by
-
What Can the Organization of the Brain's Default Mode Network Tell us About Self-Knowledge?Front Hum Neurosci. 2013 Jul 17;7:391. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00391. eCollection 2013. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23882210 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Activity Associated with Symptoms Change in Depressed Adolescents following Self-Processing Neurofeedback.Brain Sci. 2022 Aug 25;12(9):1128. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12091128. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36138864 Free PMC article.
-
When the brain is prepared to learn: enhancing human learning using real-time fMRI.Neuroimage. 2012 Jan 2;59(1):846-52. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.063. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 21821136 Free PMC article.
-
Single Voxel Proton Spectroscopy for Neurofeedback at 7 Tesla.Materials (Basel). 2011 Sep;4(9):1548-63. doi: 10.3390/ma4091548. Materials (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24416473 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness-based real-time fMRI neurofeedback: a randomized controlled trial to optimize dosing for depressed adolescents.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 17;23(1):757. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05223-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37848857 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bagarinao E, Matsuo K, Nakai T. Real-time functional MRI using a PC cluster. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance Part B: Magnetic Resonance Engineering. 2003a;19(1):14–25.
-
- Bagarinao E, Matsuo K, Nakai T, Sato S. Estimation of general linear model coefficients for real-time application. Neuroimage. 2003b;19(2):422–429. - PubMed
-
- Bagarinao E, Matsuo K, Tanaka Y, Sarmenta L, Nakai T. Enabling on-demand real-time functional MRI analysis using grid technology. Methods of Information in Medicine. 2005;44(5):665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

