Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted radioimmunotherapy of human head and neck cancer xenografts using 90Y-labeled fully human antibody panitumumab
- PMID: 20682654
- PMCID: PMC3629966
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0444
Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted radioimmunotherapy of human head and neck cancer xenografts using 90Y-labeled fully human antibody panitumumab
Abstract
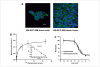
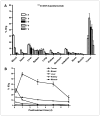
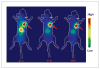
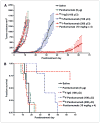
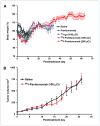
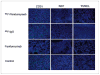
Panitumumab (ABX-EGF or Vectibix), the first fully human monoclonal antibody targeting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Here, we report for the first time the radioimmunotherapy (RIT) of EGFR-positive human head and neck cancer in a nude mouse model using pure beta(-) emitter (90)Y-labeled panitumumab. Biodistribution and planar gamma-imaging studies were carried out with (111)In-DOTA-panitumumab. The RIT efficacy of (90)Y-DOTA-panitumumab was evaluated in UM-SCC-22B tumor model. CD31, Ki67, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling, and H&E staining were done on UM-SCC-22B tumor sections after treatment. The tumor uptake of (111)In-DOTA-panitumumab in UM-SCC-22B tumor-bearing nude mice was 26.10 +/- 4.93, 59.11 +/- 7.22, 44.57 +/- 9.80, 40.38 +/- 7.76, and 14.86 +/- 7.23 % injected dose per gram of tissue at 4, 24, 72, 120, and 168 hours after injection, respectively. Immunotherapy with cold panitumumab (four doses of 10 mg/kg) did not cause significant antitumor effect. RIT with a single dose of 100 microCi (90)Y-DOTA-panitumumab caused significant tumor growth delay and improved the survival in UM-SCC-22B tumor model. A single dose of 200 microCi (90)Y-DOTA-panitumumab led to almost complete tumor regression (tumor volumes were 34.83 +/- 11.11 mm(3) and 56.02 +/- 39.95 mm(3) on days 0 and 46 after treatment, respectively). Histopathologic analysis of tumors and normal organs further validated the therapeutic efficacy and limited systemic toxicity of (90)Y-DOTA-panitumumab. The high tumor uptake and prolonged tumor retention, as well as effective therapy, reveal that (90)Y-DOTA-panitumumab may be a promising radioimmunotherapeutic agent to treat EGFR-positive solid tumors.
(c) 2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cetuximab-based immunotherapy and radioimmunotherapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 1;16(7):2095-105. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2495. Epub 2010 Mar 9. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20215534 Free PMC article.
-
177Lu-labeled antibodies for EGFR-targeted SPECT/CT imaging and radioimmunotherapy in a preclinical head and neck carcinoma model.Mol Pharm. 2014 Mar 3;11(3):800-7. doi: 10.1021/mp4005047. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Mol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24472064
-
High-linear energy transfer (LET) alpha versus low-LET beta emitters in radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors: therapeutic efficacy and dose-limiting toxicity of 213Bi- versus 90Y-labeled CO17-1A Fab' fragments in a human colonic cancer model.Cancer Res. 1999 Jun 1;59(11):2635-43. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10363986
-
111In/86Y-Labeled F(ab')2 fragment of panitumumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody directed against the extracellular domain III of the epidermal growth factor receptor.2012 Apr 30 [updated 2012 Jun 21]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Apr 30 [updated 2012 Jun 21]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 22741182 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
89Zr-Labeled p-isothiocyanatobenzyl-desferrioxamine B (Df-Bz-NCS)–conjugated panitumumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody directed against the extracellular domain III of the epidermal growth factor receptor.2012 May 4 [updated 2012 Jun 21]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 May 4 [updated 2012 Jun 21]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 22741179 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Response to Combined Molecular- and External Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC).Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;13(22):5595. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225595. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830750 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity across Metastases and Organ-Specific Response Informs Drug Efficacy and Patient Survival in Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Res. 2021 May 1;81(9):2522-2533. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3665. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33589516 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted α-Particle Radiation Therapy of HER1-Positive Disseminated Intraperitoneal Disease: An Investigation of the Human Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody, Panitumumab.Transl Oncol. 2017 Aug;10(4):535-545. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 May 31. Transl Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28577439 Free PMC article.
-
Combined treatment of the experimental human papilloma virus-16-positive cervical and head and neck cancers with cisplatin and radioimmunotherapy targeting viral E6 oncoprotein.Br J Cancer. 2013 Mar 5;108(4):859-65. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.43. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23385729 Free PMC article.
-
Combined external beam radiotherapy with carbon ions and tumor targeting endoradiotherapy.Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 6;9(52):29985-30004. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25695. eCollection 2018 Jul 6. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30042828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haddad RI, Shin DM. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1143–54. - PubMed
-
- Vokes EE, Weichselbaum RR, Lippman SM, Hong WK. Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:184–94. - PubMed
-
- Alvi A, Johnson JT. Development of distant metastasis after treatment of advanced-stage head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 1997;19:500–5. - PubMed
-
- Gold KA, Lee HY, Kim ES. Targeted therapies in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 2009;115:922–35. - PubMed
-
- Argiris A, Li Y, Forastiere A. Prognostic factors and long-term survivorship in patients with recurrent or metastatic carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 2004;101:2222–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

