A 1-year lifestyle intervention for weight loss in individuals with type 2 diabetes reduces high C-reactive protein levels and identifies metabolic predictors of change: from the Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) study
- PMID: 20682679
- PMCID: PMC2963483
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0728
A 1-year lifestyle intervention for weight loss in individuals with type 2 diabetes reduces high C-reactive protein levels and identifies metabolic predictors of change: from the Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) study
Abstract
Objective: We examined whether a 1-year intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) for weight loss reduced elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels in obese individuals with diabetes and identified metabolic and fitness predictors of hs-CRP change.
Research design and methods: Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) is an ongoing multicenter clinical trial examining the effects of weight loss achieved through ILI on cardiovascular events and overall mortality in obese/overweight adults with type 2 diabetes. We report on 1,759 Look AHEAD participants who had hs-CRP and fitness data at baseline and 1 year. Subjects were randomly assigned to ILI or to usual care (diabetes support and education [DSE]). ILI involved frequent counseling to increase moderate-intensity exercise to 175 min/week, reduce caloric and saturated fat intake, and change macronutrient composition to improve glycemic control.
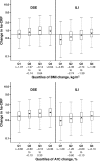
Results: ILI reduced median hs-CRP by 43.6% from baseline to 1 year, compared with a 16.7% reduction with DSE (P<0.001). ILI decreased weight (8.8%), A1C (0.7%), and triglycerides (17%) and increased fitness (19%) and HDL cholesterol (7.5%) (P<0.0001 vs. changes with DSE). Changes in adiposity and glucose control with ILI remained independent predictors of hs-CRP change at 1 year (P<0.0001 for each) after adjustment for demographics, smoking, cardiovascular history, statin and thiazolidinedione use, and changes in fitness and lipid control. Neither statin nor insulin therapy modified the association between ILI and hs-CRP.
Conclusions: A 1-year lifestyle intervention for weight loss in obese individuals with diabetes was associated with substantial reductions in hs-CRP. Improved glycemic control and reduced adiposity had comparable effects on hs-CRP change.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00017953.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lifestyle Intervention for Weight Loss and Cardiometabolic Changes in the Setting of Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Inhibition: Glucokinase Regulatory Protein-Leu446Pro Variant in Look AHEAD.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016 Feb;9(1):71-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.115.001192. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016. PMID: 26578543 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of a lifestyle intervention on change in cardiorespiratory fitness in adults with type 2 diabetes: results from the Look AHEAD Study.Int J Obes (Lond). 2009 Mar;33(3):305-16. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.280. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19153582 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lifestyle intervention and/or statins for the reduction of C-reactive protein in type 2 diabetes: from the look AHEAD study.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013 May;21(5):944-50. doi: 10.1002/oby.20431. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013. PMID: 23512860 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Look AHEAD Trial: Implications for Lifestyle Intervention in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Jul-Aug;58(1):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25936906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Look AHEAD study: a description of the lifestyle intervention and the evidence supporting it.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006 May;14(5):737-52. doi: 10.1038/oby.2006.84. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006. PMID: 16855180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammation is associated with ovarian follicular dynamics during the human menstrual cycle.PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e64807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064807. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717660 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oral magnesium supplement on cardiometabolic markers in people with prediabetes: a double blind randomized controlled clinical trial.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 28;12(1):18209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20277-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36307427 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of tooth loss with morbidity and mortality by diabetes status in older adults: a systematic review.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Oct 19;21(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00830-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 34663281 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Serum hs-CRP Levels With the Presence of Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, and Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors.J Clin Lab Anal. 2016 Sep;30(5):672-6. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21920. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2016. PMID: 26857805 Free PMC article.
-
Long Term Effect of Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Cerebral Blood Flow.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018 Jan;66(1):120-126. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15159. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018. PMID: 29082505 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott M, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Nichol G, O'Donnell C, Roger V, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J, Hong Y. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2009;119:e21–e181 - PubMed
-
- Ford ES. Body mass index, diabetes, and C-reactive protein among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 1999;22:1971–1977 - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE, Zinman B, Haffner SM, O'Neill MC, Kravitz BG, Yu D, Freed MI, Herman WH, Holman RR, Jones NP, Lachin JM, Viberti GC. ADOPT Study Group. Obesity is a major determinant of the association of C-reactive protein levels and the metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006;55:2357–2364 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM, Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT, Glynn RJ. JUPITER Study Group. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med 2008;359:2195–2207 - PubMed
-
- Esposito K, Pontillo A, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Masella M, Marfella R, Giugliano D. Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003;289:1799–1804 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

