Sequential multiplex analyte capturing for phosphoprotein profiling
- PMID: 20682761
- PMCID: PMC2984240
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.002709
Sequential multiplex analyte capturing for phosphoprotein profiling
Abstract
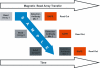
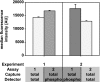
Microarray-based sandwich immunoassays can simultaneously detect dozens of proteins. However, their use in quantifying large numbers of proteins is hampered by cross-reactivity and incompatibilities caused by the immunoassays themselves. Sequential multiplex analyte capturing addresses these problems by repeatedly probing the same sample with different sets of antibody-coated, magnetic suspension bead arrays. As a miniaturized immunoassay format, suspension bead array-based assays fulfill the criteria of the ambient analyte theory, and our experiments reveal that the analyte concentrations are not significantly changed. The value of sequential multiplex analyte capturing was demonstrated by probing tumor cell line lysates for the abundance of seven different receptor tyrosine kinases and their degree of phosphorylation and by measuring the complex phosphorylation pattern of the epidermal growth factor receptor in the same sample from the same cavity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Microbead arrays for the analysis of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase activation and dimerization in breast cancer cells.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2010 Feb;8(1):27-36. doi: 10.1089/adt.2009.0208. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2010. PMID: 20035613 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating sandwich immunoassays in microarray format in terms of the ambient analyte regime.Clin Chem. 2004 Oct;50(10):1907-20. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.037929. Epub 2004 Aug 12. Clin Chem. 2004. PMID: 15308599
-
Double-chip protein arrays: force-based multiplex sandwich immunoassays with increased specificity.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2004 Aug;379(7-8):974-81. doi: 10.1007/s00216-004-2607-0. Epub 2004 Apr 21. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2004. PMID: 15103448
-
Multiplexing molecular diagnostics and immunoassays using emerging microarray technologies.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007 Jan;7(1):87-98. doi: 10.1586/14737159.7.1.87. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007. PMID: 17187487 Review.
-
Quantitative protein profiling using antibody arrays.Proteomics. 2004 Dec;4(12):3717-26. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200300877. Proteomics. 2004. PMID: 15540209 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplexed protein profiling by sequential affinity capture.Proteomics. 2016 Apr;16(8):1251-6. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201500398. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26935855 Free PMC article.
-
A dual array-based approach to assess the abundance and posttranslational modification state of signaling proteins.Sci Signal. 2012 Jan 10;5(206):pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002372. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22234610 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential multiplexed analyte quantification using peptide immunoaffinity enrichment coupled to mass spectrometry.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jun;11(6):M111.015347. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.015347. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22203691 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential Protein Capture in Multiplex Single Molecule Arrays: A Strategy for Eliminating Assay Cross-Reactivity.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Feb;10(4):e2001111. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202001111. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 32893488 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate serum proteins for classifying well-differentiated small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 25;8(11):e81712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081712. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24282616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmelzle K., White F. M. (2006) Phosphoproteomic approaches to elucidate cellular signaling networks. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 17, 406–414 - PubMed
-
- Gaudet S., Janes K. A., Albeck J. G., Pace E. A., Lauffenburger D. A., Sorger P. K. (2005) A compendium of signals and responses triggered by prodeath and prosurvival cytokines. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4, 1569–1590 - PubMed
-
- Khan I. H., Mendoza S., Rhyne P., Ziman M., Tuscano J., Eisinger D., Kung H. J., Luciw P. A. (2006) Multiplex analysis of intracellular signaling pathways in lymphoid cells by microbead suspension arrays. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 5, 758–768 - PubMed
-
- Du J., Bernasconi P., Clauser K. R., Mani D. R., Finn S. P., Beroukhim R., Burns M., Julian B., Peng X. P., Hieronymus H., Maglathlin R. L., Lewis T. A., Liau L. M., Nghiemphu P., Mellinghoff I. K., Louis D. N., Loda M., Carr S. A., Kung A. L., Golub T. R. (2009) Bead-based profiling of tyrosine kinase phosphorylation identifies SRC as a potential target for glioblastoma therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 77–83 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paweletz C. P., Charboneau L., Bichsel V. E., Simone N. L., Chen T., Gillespie J. W., Emmert-Buck M. R., Roth M. J., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Liotta L. A. (2001) Reverse phase protein microarrays which capture disease progression show activation of pro-survival pathways at the cancer invasion front. Oncogene 20, 1981–1989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

