Polarization and migration of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells rely on the RhoA/ROCK I pathway and an active reorganization of the microtubule network
- PMID: 20682776
- PMCID: PMC2951238
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.145037
Polarization and migration of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells rely on the RhoA/ROCK I pathway and an active reorganization of the microtubule network
Abstract
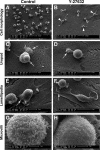
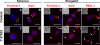
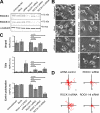
Understanding the physiological migration of hematopoietic progenitors is important, not only for basic stem cell research, but also in view of their therapeutic relevance. Here, we investigated the role of the Rho kinase pathway in the morphology and migration of hematopoietic progenitors using an ex vivo co-culture consisting of human primary CD34(+) progenitors and mesenchymal stromal cells. The addition of the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 led to the abolishment of the uropod and microvillar-like structures of hematopoietic progenitors, concomitant with a redistribution of proteins found therein (prominin-1 and ezrin). Y-27632-treated cells displayed a deficiency in migration. Time-lapse video microscopy revealed impairment of the rear pole retraction. Interestingly, the knockdown of ROCK I, but not ROCK II, using RNA interference (RNAi) was sufficient to cause the referred morphological and migrational changes. Unexpectedly, the addition of nocodazole to either Y-27632- or ROCK I RNAi-treated cells could restore their polarized morphology and migration suggesting an active role for the microtubule network in tail retraction. Finally, we could demonstrate using RNAi that RhoA, the upstream regulator of ROCK, is involved in these processes. Collectively, our data provide new insights regarding the role of RhoA/ROCK I and the microtubules in the migration of stem cells.
Figures
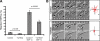


Similar articles
-
Segregation of lipid raft markers including CD133 in polarized human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.Blood. 2004 Oct 15;104(8):2332-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0511. Epub 2004 Jul 1. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15231568
-
Microtubules regulate migratory polarity through Rho/ROCK signaling in T cells.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 19;5(1):e8774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008774. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20098744 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of p-ERM and Rho-ROCK signaling in lymphocyte polarity and uropod formation.J Cell Biol. 2004 Oct 25;167(2):327-37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200403091. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15504914 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging targets in drug discovery against neurodegenerative diseases: Control of synapsis disfunction by the RhoA/ROCK pathway.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 5;225:113742. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113742. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34388381 Review.
-
Role of Rho kinases in abnormal and normal hematopoiesis.Curr Opin Hematol. 2014 Jul;21(4):271-5. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000056. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24867289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Skeletal Metastases of Unknown Primary: Biological Landscape and Clinical Overview.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 29;11(9):1270. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091270. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31470608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RHOA Therapeutic Targeting in Hematological Cancers.Cells. 2023 Jan 28;12(3):433. doi: 10.3390/cells12030433. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prominin-1 Modulates Rho/ROCK-Mediated Membrane Morphology and Calcium-Dependent Intracellular Chloride Flux.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 4;9(1):15911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52040-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31685837 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroitin Sulfate Impairs Neural Stem Cell Migration Through ROCK Activation.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Apr;55(4):3185-3195. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0565-8. Epub 2017 May 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28477140 Free PMC article.
-
CD133 is a modifier of hematopoietic progenitor frequencies but is dispensable for the maintenance of mouse hematopoietic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 2;110(14):5582-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215438110. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23509298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright D. E., Wagers A. J., Gulati A. P., Johnson F. L., Weissman I. L. (2001) Science 294, 1933–1936 - PubMed
-
- Giebel B., Corbeil D., Beckmann J., Höhn J., Freund D., Giesen K., Fischer J., Kögler G., Wernet P. (2004) Blood 104, 2332–2338 - PubMed
-
- Barreiro O., de la Fuente H., Mittelbrunn M., Sánchez-Madrid F. (2007) Immunol. Rev. 218, 147–164 - PubMed
-
- Friedl P., Entschladen F., Conrad C., Niggemann B., Zänker K. S. (1998) Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 2331–2343 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

