Direct binding of the EGF-like domain of neuregulin-1 to integrins ({alpha}v{beta}3 and {alpha}6{beta}4) is involved in neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling
- PMID: 20682778
- PMCID: PMC2951213
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.113878
Direct binding of the EGF-like domain of neuregulin-1 to integrins ({alpha}v{beta}3 and {alpha}6{beta}4) is involved in neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling
Abstract
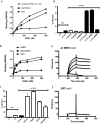
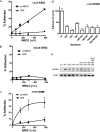
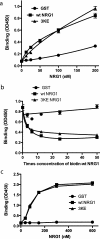
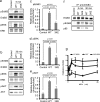
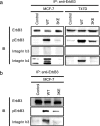
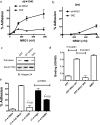
Integrin-growth factor receptor cross-talk plays a role in growth factor signaling, but the specifics are unclear. In a current model, integrins and growth factor receptors independently bind to their ligands (extracellular matrix and growth factors, respectively). We discovered that neuregulin-1 (NRG1), either as an isolated EGF-like domain or as a native multi-domain form, binds to integrins αvβ3 (with a K(D) of 1.36 × 10(-7) m) and α6β4. Docking simulation predicted that three Lys residues at positions 180, 184, and 186 of the EGF-like domain are involved in integrin binding. Mutating these residues to Glu individually or in combination markedly suppressed integrin binding and ErbB3 phosphorylation. Mutating all three Lys residues to Glu (the 3KE mutation) did not affect the ability of NRG1 to bind to ErbB3 but markedly reduced the ability of NRG1 to induce ErbB3 phosphorylation and AKT and Erk1/2 activation in MCF-7 and T47D human breast cancer cells. This suggests that direct integrin binding to NRG1 is critical for NRG1/ErbB signaling. Notably, stimulation of cells with WT NRG1 induced co-precipitation of ErbB3 with α6β4 and with αvβ3 to a much lower extent. This suggests that WT NRG1 induces integrin-NRG1-ErbB3 ternary complex formation. In contrast, the 3KE mutant was much less effective in inducing ternary complex formation than WT NRG1, suggesting that this process depends on the ability of NRG1 to bind to integrins. These results suggest that direct NRG1-integrin interaction mediates integrin-ErbB cross-talk and that α6β4 plays a major role in NRG-ErbB signaling in these cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The direct binding of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) to integrin alphavbeta3 is involved in IGF-1 signaling.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24106-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.013201. Epub 2009 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19578119 Free PMC article.
-
Direct integrin binding to insulin-like growth factor-2 through the C-domain is required for insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 (IGF1R) signaling.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 5;12(9):e0184285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184285. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28873464 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR kinase inhibition disrupts neuregulin 1-ERBB3 autocrine signaling and sensitizes NF2-deficient meningioma cellular models to IGF1R inhibition.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100157. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014960. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33273014 Free PMC article.
-
The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007;190:1-65. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17432114 Review.
-
Proteolytic processing of Neuregulin-1.Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 2):178-182. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27393467 Review.
Cited by
-
Rats, Neuregulins and Radical Prostatectomy: A Conceptual Overview.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 13;12(6):2208. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062208. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD5 Binds to Interleukin-6 and Induces a Feed-Forward Loop with the Transcription Factor STAT3 in B Cells to Promote Cancer.Immunity. 2016 Apr 19;44(4):913-923. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.04.003. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27096320 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: loss of the physiological integrin expression pattern correlates with disease progression.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 14;9(11):e109026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109026. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25398092 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding to integrins and loss of disulfide linkage in interleukin-1β (IL-1β) are involved in the agonistic action of IL-1β.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20067-20075. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.818302. Epub 2017 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29030430 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the dynamics of EMT reveals genes associated with pan-cancer intermediate states and plasticity.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025 Apr 10;11(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41540-025-00512-2. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025. PMID: 40210876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peles E., Bacus S. S., Koski R. A., Lu H. S., Wen D., Ogden S. G., Levy R. B., Yarden Y. (1992) Cell 69, 205–216 - PubMed
-
- Carraway K. L., 3rd, Weber J. L., Unger M. J., Ledesma J., Yu N., Gassmann M., Lai C. (1997) Nature 387, 512–516 - PubMed
-
- Chang H., Riese D. J., 2nd, Gilbert W., Stern D. F., McMahan U. J. (1997) Nature 387, 509–512 - PubMed
-
- Falls D. L. (2003) Exp. Cell Res. 284, 14–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

