Dual inhibition of both the epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB2 effectively inhibits the promotion of skin tumors during two-stage carcinogenesis
- PMID: 20682802
- PMCID: PMC2940063
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0010
Dual inhibition of both the epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB2 effectively inhibits the promotion of skin tumors during two-stage carcinogenesis
Abstract
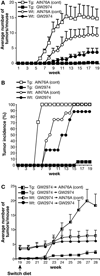
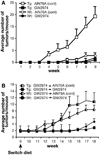
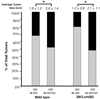
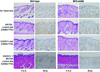
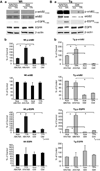
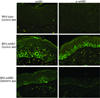
The erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases are known to play important roles in normal epithelial development and epithelial neoplasia. Considerable evidence also suggests that signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays an important role in multistage skin carcinogenesis in mice; however, less is known about the role of erbB2. In this study, to further examine the role of both erbB2 and EGFR in epithelial carcinogenesis, we examined the effect of a dual erbB2/EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, GW2974, given in the diet on skin tumor promotion during two-stage carcinogenesis in wild-type and BK5.erbB2 mice. In BK5.erbB2 mice, erbB2 is overexpressed in the basal layer of epidermis and leads to heightened sensitivity to skin tumor development. GW2974 effectively inhibited skin tumor promotion by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in wild-type and BK5.erbB2 mice, although a more marked effect was seen in BK5.erbB2 mice. In addition, this inhibitory effect was reversible when GW2974 treatment was withdrawn. GW2974 inhibited 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced epidermal hyperproliferation, which correlated with reduced activation of both the EGFR and erbB2. These results support the hypothesis that both the EGFR and erbB2 play an important role in the development of skin tumors during two-stage skin carcinogenesis, especially during the tumor promotion stage. Furthermore, the marked sensitivity of BK5.erbB2 mice to the inhibitory effects of GW2974 during tumor promotion suggest greater efficacy for this compound when erbB2 is overexpressed or amplified as an early event in the carcinogenic process.
2010 AACR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Constitutive expression of erbB2 in epidermis of transgenic mice results in epidermal hyperproliferation and spontaneous skin tumor development.Oncogene. 2000 Aug 31;19(37):4243-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203778. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10980598
-
Impact of mTORC1 inhibition on keratinocyte proliferation during skin tumor promotion in wild-type and BK5.AktWT mice.Mol Carcinog. 2014 Nov;53(11):871-82. doi: 10.1002/mc.22046. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Mol Carcinog. 2014. PMID: 24114993 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoprevention of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-induced oral carcinogenesis in hamster cheek pouch by topical application of a dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ErbB2 tyrosine kinases.Oral Oncol. 2008 Jul;44(7):652-7. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2007.08.006. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Oral Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17936675 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2011 Jun 15;207(6):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2011. PMID: 21531084 Review.
-
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jan;139:395-411. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30500458 Review.
Cited by
-
Energy balance modulates mouse skin tumor promotion through altered IGF-1R and EGFR crosstalk.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012 Oct;5(10):1236-46. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0234. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012. PMID: 22896210 Free PMC article.
-
GW-2974 and SCH-442416 modulators of tyrosine kinase and adenosine receptors can also stabilize human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 7;17(12):e0277963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277963. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36476719 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the EP receptors for prostaglandin E2 in skin and skin cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011 Dec;30(3-4):465-80. doi: 10.1007/s10555-011-9317-9. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011. PMID: 22012553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aaronson SA. Growth factors and cancer. Science. 1991;254:1146–1153. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J, Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992;9:389–391. - PubMed
-
- Ullrich A, Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990;61:203–212. - PubMed
-
- Gullick WJ. Prevalence of aberrant expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human cancers. Br Med Bull. 1991;47:87–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

