Severe multifocal form of buruli ulcer after streptomycin and rifampin treatment: comments on possible dissemination mechanisms
- PMID: 20682873
- PMCID: PMC2911176
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0617
Severe multifocal form of buruli ulcer after streptomycin and rifampin treatment: comments on possible dissemination mechanisms
Abstract
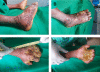
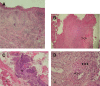
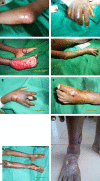
Buruli ulcer (BU), a disease caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans, leads to the destruction of skin and sometimes bone. Here, we report a case of severe multifocal BU with osteomyelitis in a 6-year-old human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-negative boy. Such disseminated forms are poorly documented and generally occur in patients with HIV co-infection. The advent of antibiotic treatment with streptomycin (S) and rifampin (R) raised hope that these multifocal BU cases could be reduced. The present case raises two relevant points about multifocal BU: the mechanism of dissemination that leads to the development of multiple foci and the difficulties of treatment of multifocal forms of BU. Biochemical (hypoproteinemia), hematological (anemia), clinical (traditional treatment), and genetic factors are discussed as possible risk factors for dissemination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treating Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer): from surgery to antibiotics, is the pill mightier than the knife?Future Microbiol. 2011 Oct;6(10):1185-98. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.101. Future Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22004037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcome of Streptomycin-Rifampicin treatment of Buruli Ulcer in two Ghanaian districts.Pan Afr Med J. 2016 Oct 1;25(Suppl 1):13. doi: 10.11604/pamj.supp.2016.25.1.6203. eCollection 2016. Pan Afr Med J. 2016. PMID: 28149438 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes of Ghanaian Buruli ulcer patients who defaulted from antimicrobial therapy.Trop Med Int Health. 2016 Sep;21(9):1191-6. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12745. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Trop Med Int Health. 2016. PMID: 27456068
-
Promising clinical efficacy of streptomycin-rifampin combination for treatment of buruli ulcer (Mycobacterium ulcerans disease).Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Nov;51(11):4029-35. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00175-07. Epub 2007 May 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17526760 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Buruli ulcer in West Africa: strategies for early detection and treatment in the antibiotic era.East Afr J Public Health. 2009 Aug;6(2):144-7. doi: 10.4314/eajph.v6i2.51744. East Afr J Public Health. 2009. PMID: 20000019 Review.
Cited by
-
Corticosteroid-induced immunosuppression ultimately does not compromise the efficacy of antibiotherapy in murine Mycobacterium ulcerans infection.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(11):e1925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001925. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 23209864 Free PMC article.
-
Treating Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer): from surgery to antibiotics, is the pill mightier than the knife?Future Microbiol. 2011 Oct;6(10):1185-98. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.101. Future Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22004037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burden and Historical Trend of Buruli Ulcer Prevalence in Selected Communities along the Offin River of Ghana.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Apr 14;10(4):e0004603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004603. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27078028 Free PMC article.
-
Phage therapy as a renewed therapeutic approach to mycobacterial infections: a comprehensive review.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Sep 17;12:2943-2959. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S218638. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31571947 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of human immunodeficiency virus on the severity of buruli ulcer disease: results of a retrospective study in cameroon.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014 May 21;1(1):ofu021. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofu021. eCollection 2014 Mar. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25734094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lagarrigue V, Portaels F, Meyers WM, Aguiar J. Buruli ulcer: risk of bone involvement! A propos of 33 cases observed in Benin. Méd Trop. 2000;60:262–266. - PubMed
-
- Portaels F, Zinsou C, Aguiar J, Debacker M, de Biurrun E, Guédénon A, Josse R, Lagarrigue V, Silva MT, Steunou C, Meyers WM. Les atteintes osseuses de l'ulcère de Buruli: à propos de 73 cas. Bull Seances Acad R Sci Outre Mer. 2003;49:161–190.
-
- World Health Organization . In: A Manual for Health Care Providers. Portaels F, Johnson P, Meyers WM, editors. Geneva: WHO/CDS/CPE/GBUI/2001.4; 2001. (Buruli ulcer. Diagnosis of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease).
-
- Walsh DS, Portaels F, Meyers WM. Buruli ulcer (Mycobacterium ulcerans infection) Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2008;102:969–978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

