Arabidopsis S6 kinase mutants display chromosome instability and altered RBR1-E2F pathway activity
- PMID: 20683442
- PMCID: PMC2944053
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.164
Arabidopsis S6 kinase mutants display chromosome instability and altered RBR1-E2F pathway activity
Abstract
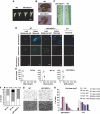
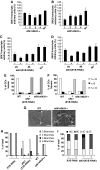
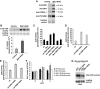
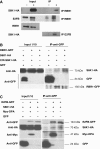
The 40S ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) is a conserved component of signalling pathways controlling growth in eukaryotes. To study S6K function in plants, we isolated single- and double-knockout mutations and RNA-interference (RNAi)-silencing lines in the linked Arabidopsis S6K1 and S6K2 genes. Hemizygous s6k1s6k2/++ mutant and S6K1 RNAi lines show high phenotypic instability with variation in size, increased trichome branching, produce non-viable pollen and high levels of aborted seeds. Analysis of their DNA content by flow cytometry, as well as chromosome counting using DAPI staining and fluorescence in situ hybridization, revealed an increase in ploidy and aneuploidy. In agreement with this data, we found that S6K1 associates with the Retinoblastoma-related 1 (RBR1)-E2FB complex and this is partly mediated by its N-terminal LVxCxE motif. Moreover, the S6K1-RBR1 association regulates RBR1 nuclear localization, as well as E2F-dependent expression of cell cycle genes. Arabidopsis cells grown under nutrient-limiting conditions require S6K for repression of cell proliferation. The data suggest a new function for plant S6K as a repressor of cell proliferation and required for maintenance of chromosome stability and ploidy levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bettencourt-Dias M, Giet R, Sinka R, Mazumdar A, Lock WG, Balloux F, Zafiropoulos PJ, Yamaguchi S, Winter S, Carthew RW, Cooper M, Jones D, Frenz L, Glover DM (2004) Genome-wide survey of protein kinases required for cell cycle progression. Nature 432: 980–987 - PubMed
-
- Bögre L, Ökrész L, Henriques R, Anthony RG (2003) Growth signalling pathways in Arabidopsis and the AGC protein kinases. Trends Plant Sci 8: 424–431 - PubMed
-
- Bonatti S, Simili M, Galli A, Bagnato P, Pigullo S, Schiestl RH, Abbondandolo A (1998) Inhibition of the Mr 70 000 S6 kinase pathway by rapamycin results in chromosome malsegregation in yeast and mammalian cells. Chromosoma 107: 498–506 - PubMed
-
- Boudolf V, Vlieghe K, Beemster GTS, Magyar Z, Acosta JAT, Maes S, Van Der Schueren E, Inze D, De Veylder L (2004) The plant-specific cyclin-dependent kinase CDKB1;1 and transcription factor E2Fa-DPa control the balance of mitotically dividing and endoreduplicating cells in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16: 2683–2692 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

