Whole blood-derived miRNA profiles as potential new tools for ovarian cancer screening
- PMID: 20683447
- PMCID: PMC2938264
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605833
Whole blood-derived miRNA profiles as potential new tools for ovarian cancer screening
Abstract
Background: Screening is an unsolved problem for ovarian cancer (OvCA). As late detection is equivalent to poor prognosis, we analysed whether OvCA patients show diagnostically meaningful microRNA (miRNA) patterns in blood cells.
Methods: Blood-borne whole miRNome profiles from 24 patients with OvCA and 15 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were biostatistically evaluated.
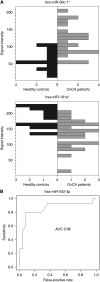
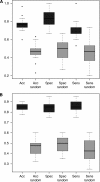
Results: Student's t-test revealed 147 significantly deregulated miRNAs before and 4 after Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment. Although these included miRNAs already linked to OvCA (e.g., miR-16, miR-155), others had never before been connected to specific diseases. A bioinformatically calculated miRNA profile allowed for discrimination between blood samples of OvCA patients and healthy controls with an accuracy of >76%. When only cancers of the serous subtype were considered and compared with an extended control group (n=39), accuracy, specificity and sensitivity all increased to >85%.
Conclusion: Our proof-of-principle study strengthens the hypothesis that neoplastic diseases generate characteristic miRNA fingerprints in blood cells. Still, the obtained OvCA-associated miRNA pattern is not yet sensitive and specific enough to permit the monitoring of disease progression or even preventive screening. Microarray-based miRNA profiling from peripheral blood could thus be combined with other markers to improve the notoriously difficult but important screening for OvCA.
Conflict of interest statement
AK and MS are also affiliates of febit biome GmbH as Vice President and Vice President of sales, respectively. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A specific miRNA signature in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients.J Neurochem. 2011 Aug;118(3):449-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07307.x. Epub 2011 Jun 17. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21561454
-
Identification of stably expressed reference small non-coding RNAs for microRNA quantification in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma tissues.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Dec;20(12):2341-2348. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12927. Epub 2016 Jul 15. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27419385 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based markers for early stage breast cancer detection.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029770. Epub 2012 Jan 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22242178 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miR-200b in ovarian carcinoma patients: distinct pattern of pre/post-treatment variation compared to CA-125 and potential for prediction of progression-free survival.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 3;6(34):36815-24. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5766. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26416421 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer.Mol Cancer. 2016 Jun 24;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0536-0. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27343009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-125b Regulation of Androgen Receptor Signaling Via Modulation of the Receptor Complex Co-Repressor NCOR2.Biores Open Access. 2012 Apr;1(2):55-62. doi: 10.1089/biores.2012.9903. Biores Open Access. 2012. PMID: 23514806 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-200c as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer.J Transl Med. 2012 Sep 6;10:186. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-186. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22954417 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Biopsies for Ovarian Carcinoma: How Blood Tests May Improve the Clinical Management of a Deadly Disease.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 4;11(6):774. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060774. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31167492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs: potential biomarkers for cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(3):2055-63. doi: 10.3390/ijms12032055. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21673939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The deterministic role of 5-mers in microRNA-gene targeting.RNA Biol. 2018;15(6):819-825. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1462652. Epub 2018 May 11. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 29749304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, Pasini B, Radice P, Manoukian S, Eccles DM, Tang N, Olah E, Anton-Culver H, Warner E, Lubinski J, Gronwald J, Gorski B, Tulinius H, Thorlacius S, Eerola H, Nevanlinna H, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi OP, Thompson D, Evans C, Peto J, Lalloo F, Evans DG, Easton DF (2003) Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet 72: 1117–1130 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antoniou AC, Cunningham AP, Peto J, Evans DG, Lalloo F, Narod SA, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Southey MC, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, Pasini B, Radice P, Manoukian S, Eccles DM, Tang N, Olah E, Anton-Culver H, Warner E, Lubinski J, Gronwald J, Gorski B, Tryggvadottir L, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi OP, Eerola H, Nevanlinna H, Pharoah PD, Easton DF (2008) The BOADICEA model of genetic susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancers: updates and extensions. Br J Cancer 98: 1457–1466 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bast Jr RC, Klug TL, St John E, Jenison E, Niloff JM, Lazarus H, Berkowitz RS, Leavitt T, Griffiths CT, Parker L, Zurawski Jr VR, Knapp RC (1983) A radioimmunoassay using a monoclonal antibody to monitor the course of epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 309: 883–887 - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, Golani I (2001) Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav Brain Res 125: 279–284 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

