Analysis of plant diversity with retrotransposon-based molecular markers
- PMID: 20683483
- PMCID: PMC3183911
- DOI: 10.1038/hdy.2010.93
Analysis of plant diversity with retrotransposon-based molecular markers
Abstract
Retrotransposons are both major generators of genetic diversity and tools for detecting the genomic changes associated with their activity because they create large and stable insertions in the genome. After the demonstration that retrotransposons are ubiquitous, active and abundant in plant genomes, various marker systems were developed to exploit polymorphisms in retrotransposon insertion patterns. These have found applications ranging from the mapping of genes responsible for particular traits and the management of backcrossing programs to analysis of population structure and diversity of wild species. This review provides an insight into the spectrum of retrotransposon-based marker systems developed for plant species and evaluates the contributions of retrotransposon markers to the analysis of population diversity in plants.
Figures

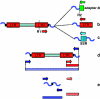
References
-
- Antonius-Klemola K, Kalendar R, Schulman AH. TRIM retrotransposons occur in apple and are polymorphic between varieties but not sports. Theor Appl Genet. 2006;112:999–1008. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- Baumel A, Ainouche M, Kalendar R, Schulman AH. Retrotransposons and genomic stability in populations of the young allopolyploid species Spartina anglica C.E. Hubbard (Poaceae) Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:1218–1227. - PubMed
-
- Bernet GP, Asins MJ. Identification and genomic distribution of gypsy like retrotransposons in Citrus and Poncirus. Theor Appl Genet. 2004;108:121–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

