Physiological carbon dioxide, bicarbonate, and pH sensing
- PMID: 20683624
- PMCID: PMC2967379
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-010-0865-6
Physiological carbon dioxide, bicarbonate, and pH sensing
Abstract
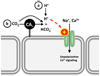
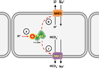
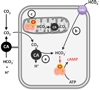
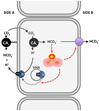
In biological systems, carbon dioxide exists in equilibrium with bicarbonate and protons. The individual components of this equilibrium (i.e., CO₂, HCO₃⁻, and H(+)), which must be sensed to be able to maintain cellular and organismal pH, also function as signals to modulate multiple physiological functions. Yet, the molecular sensors for CO₂/HCO₃⁻/pH remained unknown until recently. Here, we review recent progress in delineating molecular and cellular mechanisms for sensing CO₂, HCO₃⁻, and pH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physiological sensing of carbon dioxide/bicarbonate/pH via cyclic nucleotide signaling.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(2):2112-28. doi: 10.3390/s110202112. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 21544217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of acid-base sensing by the kidney.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 May;23(5):774-80. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012010029. Epub 2012 Feb 23. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22362904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing inorganic carbon: CO2 and HCO3-.Biochem J. 2006 Jun 1;396(2):e5-7. doi: 10.1042/bj20060574. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16703664 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological roles of acid-base sensors.Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:347-62. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071821. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25340964 Review.
-
Role of Na(+)HCO(3)(-) cotransporter NBC1, Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1, and carbonic anhydrase in rabbit duodenal bicarbonate secretion.Gastroenterology. 2000 Aug;119(2):406-19. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.9358. Gastroenterology. 2000. PMID: 10930376
Cited by
-
Transmembrane Transport of Bicarbonate by Anion Receptors.Chempluschem. 2022 Nov;87(11):e202200266. doi: 10.1002/cplu.202200266. Chempluschem. 2022. PMID: 36414387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupting proton dynamics and energy metabolism for cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Sep;13(9):611-23. doi: 10.1038/nrc3579. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23969692 Review.
-
Advances in anion binding and sensing using luminescent lanthanide complexes.Chem Sci. 2021 Jan 26;12(8):2716-2734. doi: 10.1039/d0sc05419d. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34164038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of acute acid-base disturbances on the phosphorylation of phospholipase C-γ1 and Erk1/2 in the renal proximal tubule.Physiol Rep. 2015 Mar;3(3):e12280. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12280. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25780091 Free PMC article.
-
The Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor Ethoxzolamide Inhibits the Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR Regulon and Esx-1 Secretion and Attenuates Virulence.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Aug;59(8):4436-45. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00719-15. Epub 2015 May 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25987613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roos A, Boron WF. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981;61:296–434. - PubMed
-
- Casey JR, Grinstein S, Orlowski J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2101;11:50–61. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig MG, Vanek M, Guerini D, Gasser JA, Jones CE, Junker U, Hofstetter H, Wolf RM, Seuwen K. Proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 2003;425:93–98. - PubMed
-
- Wang J-Q, Kon J, Mogi C, Tobo M, Damirin A, Sato K, Komachi M, Malchinkhuu E, Murata N, Kimura T, Kuwabara A, Wakamatsu K, Koizumi H, Uede T, Tsujimoto G, Kurose H, Sato T, Harada A, Misawa N, Tomura H, Okajima F. TDAG8 is a proton-sensing and psychosine-sensitive G-protein-coupled receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:45626–45633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

