Mutation at a strictly conserved, active site tyrosine in the copper amine oxidase leads to uncontrolled oxygenase activity
- PMID: 20684524
- PMCID: PMC2927706
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100643y
Mutation at a strictly conserved, active site tyrosine in the copper amine oxidase leads to uncontrolled oxygenase activity
Abstract
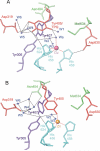
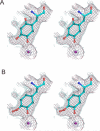
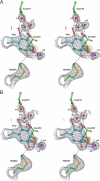
The copper amine oxidases carry out two copper-dependent processes: production of their own redox-active cofactor (2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine quinone, TPQ) and the subsequent oxidative deamination of substrate amines. Because the same active site pocket must facilitate both reactions, individual active site residues may serve multiple roles. We have examined the roles of a strictly conserved active site tyrosine Y305 in the copper amine oxidase from Hansenula polymorpha kinetically, spetroscopically (Dubois and Klinman (2006) Biochemistry 45, 3178), and, in the present work, structurally. While the Y305A enzyme is almost identical to the wild type, a novel, highly oxygenated species replaces TPQ in the Y305F active sites. This new structure not only provides the first direct detection of peroxy intermediates in cofactor biogenesis but also indicates the critical control of oxidation chemistry that can be conferred by a single active site residue.
Figures

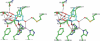
Similar articles
-
Role of a strictly conserved active site tyrosine in cofactor genesis in the copper amine oxidase from Hansenula polymorpha.Biochemistry. 2006 Mar 14;45(10):3178-88. doi: 10.1021/bi052025m. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16519513
-
Mutation of a strictly conserved, active-site residue alters substrate specificity and cofactor biogenesis in a copper amine oxidase.Biochemistry. 1999 Mar 23;38(12):3683-93. doi: 10.1021/bi982199m. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10090756
-
Investigation of spectroscopic intermediates during copper-binding and TPQ formation in wild-type and active-site mutants of a copper-containing amine oxidase from yeast.Biochemistry. 2000 Apr 4;39(13):3690-8. doi: 10.1021/bi992225w. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10736168
-
Structure and biogenesis of topaquinone and related cofactors.J Biol Inorg Chem. 1999 Feb;4(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s007750050283. J Biol Inorg Chem. 1999. PMID: 10499097 Review.
-
Copper amine oxidase: a novel use for a tyrosine.Structure. 1995 Nov 15;3(11):1127-9. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00247-7. Structure. 1995. PMID: 8591022 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the Preprocessed Copper Site Equilibrium in Amine Oxidase and Assignment of the Reactive Copper Site in Topaquinone Biogenesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Jun 5;141(22):8877-8890. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01922. Epub 2019 May 28. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31060358 Free PMC article.
-
Intrigues and intricacies of the biosynthetic pathways for the enzymatic quinocofactors: PQQ, TTQ, CTQ, TPQ, and LTQ.Chem Rev. 2014 Apr 23;114(8):4343-65. doi: 10.1021/cr400475g. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24350630 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Copper active sites in biology.Chem Rev. 2014 Apr 9;114(7):3659-853. doi: 10.1021/cr400327t. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 24588098 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Activation of dioxygen by copper metalloproteins and insights from model complexes.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017 Apr;22(2-3):253-288. doi: 10.1007/s00775-016-1415-2. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 27921179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of protein crystallography in defining the mechanisms of biogenesis and catalysis in copper amine oxidase.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(5):5375-5405. doi: 10.3390/ijms13055375. Epub 2012 May 3. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22754303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klinman JP, Mu D. Quinoenzymes in biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994;63:299–344. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann C, Dooley DM. Detection of reaction intermediates in topa quinone enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1995;258:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Janes SM, Mu D, Wemmer D, Smith AJ, Kaur S, Maltby D, Burlingame AL, Klinman JP. A new redox cofactor in eukaryotic enzymes: 6-hydroxydopa at the active site of bovine serum amine oxidase. Science. 1990;248:981–987. - PubMed
-
- Mu D, Janes SM, Smith AJ, Brown DE, Dooley DM, Klinman JP. Tyrosine codon corresponds to topa quinone at the active site of copper amine oxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:7979–7982. - PubMed
-
- Cai D, Klinman JP. Evidence for a self-catalytic mechanism of 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine quinone biogenesis in yeast copper amine oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:32039–32042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

