Nonpeptidic and potent small-molecule inhibitors of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP proteins
- PMID: 20684551
- PMCID: PMC2936695
- DOI: 10.1021/jm100487z
Nonpeptidic and potent small-molecule inhibitors of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP proteins
Abstract
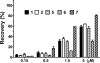
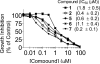
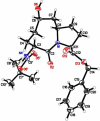
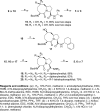
A series of compounds were designed and synthesized as antagonists of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP based upon our previously identified lead compound SM-122 (1). The most potent of these (7) binds to XIAP, cIAP-1, and cIAP-2 proteins with K(i) values of 36, <1, and <1.9 nM, respectively. Consistent with its potent binding affinities to IAPs, 7 effectively antagonizes XIAP in a cell-free caspase-9 functional assay, efficiently induces cIAP-1 degradation in cells at concentrations as low as 10 nM, and triggers activation of caspases and PARP cleavage in the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. Compound 7 potently inhibits cell growth in the MDA-MB-231 cancer cell line with an IC(50) value of 200 nM and is 9 times more potent than compound 1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of potent, nonpeptidic mimetics of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases.J Med Chem. 2009 Feb 12;52(3):593-6. doi: 10.1021/jm801101z. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19138149 Free PMC article.
-
Bivalent Smac mimetics with a diazabicyclic core as highly potent antagonists of XIAP and cIAP1/2 and novel anticancer agents.J Med Chem. 2012 Jan 12;55(1):106-14. doi: 10.1021/jm201072x. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22148838
-
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of tricyclic, conformationally constrained small-molecule mimetics of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases.J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 11;51(23):7352-5. doi: 10.1021/jm801146d. J Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 19012392 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of apoptotic proteins: new targets for anticancer therapy.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013 Sep;82(3):243-51. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12176. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013. PMID: 23790005 Review.
-
Targeting XIAP for the treatment of malignancy.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Feb;13(2):179-88. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401826. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16322751 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of drug sensitization to TRA-8, an agonistic death receptor 5 antibody, involve modulation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in human breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Apr;9(4):403-17. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0133. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21357440 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable protein interaction sites are more predisposed to surface pocket formation than the rest of the protein surface.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(3):e1002951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002951. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23505360 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl-fluorosulfate-based Lysine Covalent Pan-Inhibitors of Apoptosis Protein (IAP) Antagonists with Cellular Efficacy.J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 24;62(20):9188-9200. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01108. Epub 2019 Oct 8. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31550155 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a Potent and Orally Bioavailable Lys-Covalent Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (IAP) Antagonist.J Med Chem. 2023 Jun 22;66(12):8159-8169. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00467. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37262387 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the intermolecular recognition mechanism between the E3 ubiquitin ligase Keap1 and substrate based on multiple substrates analysis.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Dec;28(12):1233-45. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9799-y. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 25301376
References
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;1:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Salvesen GS, Duckett CS. IAP proteins: blocking the road to death's door. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Fotin-Mleczek M, Henkler F, Samel D, Reichwein M, Hausser A, Parmryd I, Scheurich P, Schmid JA, Wajant H. Apoptotic crosstalk of TNF receptors: TNF-R2-induces depletion of TRAF2 and IAP proteins and accelerates TNF-R1-dependent activation of caspase-8. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:2757–2770. - PubMed
-
- Deng Y, Ren X, Yang L, Lin Y, Wu X. A JNK-dependent pathway is required for TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Cell. 2003;115:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Holcik M, Gibson H, Korneluk RG. XIAP: Apoptotic brake and promising therapeutic target. Apoptosis. 2001;6:253–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

