Widespread cortical expression of MANF by AAV serotype 7: localization and protection against ischemic brain injury
- PMID: 20685313
- PMCID: PMC2925275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.05.020
Widespread cortical expression of MANF by AAV serotype 7: localization and protection against ischemic brain injury
Abstract
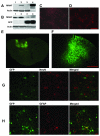
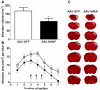
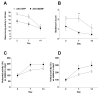
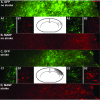
Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) is a secreted protein which reduces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and has neurotrophic effects on dopaminergic neurons. Intracortical delivery of recombinant MANF protein protects tissue from ischemic brain injury in vivo. In this study, we examined the protective effect of adeno-associated virus serotype 7 encoding MANF in a rodent model of stroke. An AAV vector containing human MANF cDNA (AAV-MANF) was constructed and verified for expression of MANF protein. AAV-MANF or an AAV control vector was administered into three sites in the cerebral cortex of adult rats. One week after the vector injections, the right middle cerebral artery (MCA) was ligated for 60min. Behavioral monitoring was conducted using body asymmetry analysis, neurological testing, and locomotor activity. Standard immunohistochemical and western blotting procedures were conducted to study MANF expression. Our data showed that AAV-induced MANF expression is redistributed in neurons and glia in cerebral cortex after ischemia. Pretreatment with AAV-MANF reduced the volume of cerebral infarction and facilitated behavioral recovery in stroke rats. In conclusion, our data suggest that intracortical delivery of AAV-MANF increases MANF protein production and reduces ischemic brain injury. Ischemia also caused redistribution of AAV-mediated MANF protein suggesting an injury-induced release.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
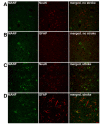
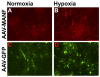
References
-
- Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke. 1986;17:472–476. - PubMed
-
- Borlongan CV, Tajima Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Sanberg PR. Cerebral ischemia and CNS transplantation: differential effects of grafted fetal rat striatal cells and human neurons derived from a clonal cell line. Neuroreport. 1998;9:3703–3709. - PubMed
-
- Chang CF, Lin SZ, Chiang YH, Morales M, Chou J, Lein P, Chen HL, Hoffer BJ, Wang Y. Intravenous administration of bone morphogenetic protein-7 after ischemia improves motor function in stroke rats. Stroke. 2003;34:558–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

