Synthesis and functional analysis of novel bivalent estrogens
- PMID: 20685325
- PMCID: PMC2948962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.019
Synthesis and functional analysis of novel bivalent estrogens
Abstract
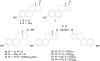
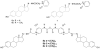
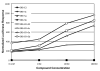
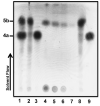
The steroid hormone estrogen plays a critical role in female development and homeostasis. Estrogen mediates its effects through binding and activation of specific estrogen receptors alpha (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta), members of the steroid/nuclear receptor family of ligand-induced transcription factors. Due to their intimate roles in genomic and nongenomic signaling pathways, these hormones and their receptors have been also implicated in the pathologies of a variety of cancers and metabolic disorders, and have been the target of large therapeutic development efforts. The binding of estrogen to its respective receptors initiates a cascade of events that include receptor dimerization, nuclear localization, DNA binding and recruitment of co-regulatory protein complexes. In this manuscript, we investigate the potential for manipulating steroid receptor gene expression activity through the development of bivalent steroid hormones that are predicted to facilitate hormone receptor dimerization events. Data are presented for the development and testing of novel estrogen dimers, linked through their C-17 moiety, that can activate estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha)-mediated transcription events with efficacy and potency equal to or greater than that of ERalpha's cognate ligand, 17beta-estradiol. These bivalent estrogen structures open the door to the development of a variety of steroid therapeutics that could dramatically impact future drug development in this area.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, et al. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:905–31. - PubMed
-
- Katzenellenbogen BS, Choi I, Delage-Mourroux R, et al. Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;74:279–85. - PubMed
-
- Levin ER. Cellular functions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Steroids. 2002;67:471–5. - PubMed
-
- Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB, Smith HO, Oprea TI, Sklar LA, Hathaway HJ. Estrogen signaling through the transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor GPR30. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:165–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

