Molecular mechanisms of antithrombin-heparin regulation of blood clotting proteinases. A paradigm for understanding proteinase regulation by serpin family protein proteinase inhibitors
- PMID: 20685328
- PMCID: PMC2974786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.05.011
Molecular mechanisms of antithrombin-heparin regulation of blood clotting proteinases. A paradigm for understanding proteinase regulation by serpin family protein proteinase inhibitors
Abstract
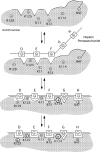
Serpin family protein proteinase inhibitors regulate the activity of serine and cysteine proteinases by a novel conformational trapping mechanism that may itself be regulated by cofactors to provide a finely-tuned time and location-dependent control of proteinase activity. The serpin, antithrombin, together with its cofactors, heparin and heparan sulfate, perform a critical anticoagulant function by preventing the activation of blood clotting proteinases except when needed at the site of a vascular injury. Here, we review the detailed molecular understanding of this regulatory mechanism that has emerged from numerous X-ray crystal structures of antithrombin and its complexes with heparin and target proteinases together with mutagenesis and functional studies of heparin-antithrombin-proteinase interactions in solution. Like other serpins, antithrombin achieves specificity for its target blood clotting proteinases by presenting recognition determinants in an exposed reactive center loop as well as in exosites outside the loop. Antithrombin reactivity is repressed in the absence of its activator because of unfavorable interactions that diminish the favorable RCL and exosite interactions with proteinases. Binding of a specific heparin or heparan sulfate pentasaccharide to antithrombin induces allosteric activating changes that mitigate the unfavorable interactions and promote template bridging of the serpin and proteinase. Antithrombin has thus evolved a sophisticated means of regulating the activity of blood clotting proteinases in a time and location-dependent manner that exploits the multiple conformational states of the serpin and their differential stabilization by glycosaminoglycan cofactors.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Gettins P. Serpin Structure, Mechanism, and Function. Chem. Rev. 2002;102:4751–4803. - PubMed
-
- Huntington JA. Shape-shifting serpins-advantages of a mobile mechanism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006;31:427–435. - PubMed
-
- Irving JA, Pike RN, Dai W, Bromme D, Worrall DM, Silverman GA, Coetzer THT, Dennison C, Bottomley SP, Whisstock JC. Evidence That Serpin Architecture Intrinsically Supports Papain-like Cysteine Protease Inhibition: Engineering α1-Antitrypsin To Inhibit Cathepsin Proteases. Biochemistry. 2002;41:4998–5004. - PubMed
-
- Björk I, Olson ST. Antithrombin. A Bloody Important Serpin. In: Church FC, Cunningham DD, Ginsburg D, Hoffman M, Stone SR, Tollefsen DM, editors. Chemistry and Biology of Serpins. Plenum Press; New York: 1997. pp. 17–33. - PubMed
-
- Church FC, Pike RN, Tollefsen DM, Buckle DM, Ciaccia AV, Olson ST. Regulation of hemostasis by heparin-binding serpins. In: Silverman GA, Lomas DA, editors. Molecular and Cellular Aspects of the Serpinopathies and Disorders of Serpin Activity. World Scientific Publishing; Singapore: 2007. pp. 509–554.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

