Interferon-gamma-mediated inhibition of serum response factor-dependent smooth muscle-specific gene expression
- PMID: 20685657
- PMCID: PMC2952243
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.164863
Interferon-gamma-mediated inhibition of serum response factor-dependent smooth muscle-specific gene expression
Abstract
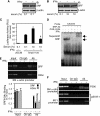
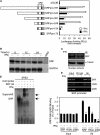
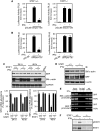
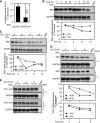
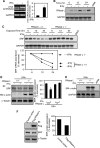
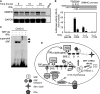
IFNγ exerts multiple biological effects on effector cells by regulating many downstream genes, including smooth muscle-specific genes. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying IFNγ-induced inhibition of smooth muscle-specific gene expression remain unclear. In this study, we have shown that serum response factor (SRF), a common transcriptional factor important in cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, is targeted by IFNγ in a STAT1-dependent manner. We show that the molecular mechanism by which IFNγ regulates SRF is via activation of the 2-5A-RNase L system, which triggers SRF mRNA decay and reduced SRF expression. As a result, decreased SRF expression reduces expression of SRF target genes such as smooth muscle α-actin and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain. Additionally, IFNγ reduced p300 and acetylated histone-3 binding in both smooth muscle α-actin and SRF promoters, epigenetically decreasing smooth muscle α-actin and SRF transcriptional activation. Our data reveal that SRF is a novel IFNγ-regulated gene and further elucidate the molecular pathway between IFNγ, IFNγ-regulated genes, and SRF and its target genes.
Figures

References
-
- Boehm U., Klamp T., Groot M., Howard J. C. (1997) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 749–795 - PubMed
-
- Dunn G. P., Koebel C. M., Schreiber R. D. (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 836–848 - PubMed
-
- Schroder K., Hertzog P. J., Ravasi T., Hume D. A. (2004) J. Leukocyte Biol. 75, 163–189 - PubMed
-
- Owens G. K., Kumar M. S., Wamhoff B. R. (2004) Physiol. Rev. 84, 767–801 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

