Nicotine worsens the severity of nephropathy in diabetic mice: implications for the progression of kidney disease in smokers
- PMID: 20685820
- PMCID: PMC3774343
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00293.2010
Nicotine worsens the severity of nephropathy in diabetic mice: implications for the progression of kidney disease in smokers
Abstract
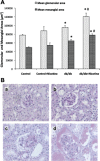
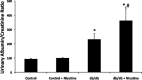
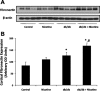
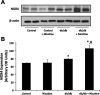
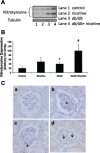
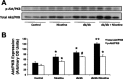
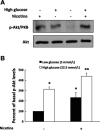
Epidemiological studies have established the role of cigarette smoking as a risk factor in the progression of chronic kidney disease, including diabetic nephropathy. We have previously reported that nicotine promotes mesangial cell proliferation and hypertrophy via activation of nonneuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and that nicotine worsens renal injury in a model of acute glomerulonephritis (Jaimes E, Tian RX, Raij L. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292: H76-H82, 2007; Jaimes EA, Tian RX, Joshi M, Raij L. Am J Nephrol 29: 319-326, 2009). These studies were designed to test the hypothesis that nicotine worsens renal injury in db/db mice, a well-established model of diabetic nephropathy, and that reactive oxygen species play an important as mediators of these effects. For these studies, nicotine (100 μg/ml) was administered in the drinking water to control and db/db mice for 10 wk. Blood pressure was measured by the tail-cuff method, and urine was collected for proteinuria. At death, kidneys were collected for histology and molecular biology. The administration of nicotine did not result in significant changes in blood pressure or blood glucose and resulted in cotinine levels similar to those found in the plasma of smokers. In diabetic mice, the administration of nicotine significantly increased urinary protein excretion (1-fold), glomerular hypertrophy, and mesangial area (∼20%). These changes were accompanied by significant increases in NADPH oxidase 4 (∼30%) and increased nitrotyrosine and Akt expression. In vitro, we determined that nicotine has additive effects to high glucose on reactive oxygen species generation and Akt phosphorylation in human mesangial cells. These findings unveil novel mechanisms that may result in the development of novel strategies in the treatment and prevention of diabetic nephropathy in smokers.
Figures
References
-
- Ago T, Kitazono T, Kuroda J, Kumai Y, Kamouchi M, Ooboshi H, Wakisaka M, Kawahara T, Rokutan K, Ibayashi S, Iida M. NAD(P)H oxidases in rat basilar arterial endothelial cells. Stroke 36: 1040–1046, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Arredondo J, Hall LL, Ndoye A, Nguyen VT, Chernyavsky AI, Bercovich D, Orr-Urtreger A, Beaudet AL, Grando SA. Central role of fibroblast alpha3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in mediating cutaneous effects of nicotine. Lab Invest 83: 207–225, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Asaba K, Tojo A, Onozato ML, Goto A, Quinn MT, Fujita T, Wilcox CS. Effects of NADPH oxidase inhibitor in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 67: 1890–1898, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87: 245–313, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bleyer AJ, Shemanski LR, Burke GL, Hansen KJ, Appel RG. Tobacco, hypertension, and vascular disease: risk factors for renal functional decline in an older population. Kidney Int 57: 2072–2079, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

