TRPC6 channels and their binding partners in podocytes: role in glomerular filtration and pathophysiology
- PMID: 20685822
- PMCID: PMC2957253
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00298.2010
TRPC6 channels and their binding partners in podocytes: role in glomerular filtration and pathophysiology
Abstract
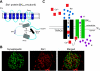
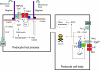
Loss or dysfunction of podocytes is a major cause of glomerular kidney disease. Several genetic forms of glomerular disease are caused by mutations in genes that encode structural elements of the slit diaphragm or the underlying cytoskeleton of podocyte foot processes. The recent discovery that gain-of-function mutations in Ca(2+)-permeable canonical transient receptor potential-6 channels (TRPC6) underlie a subset of familial forms of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) has focused attention on the basic cellular physiology of podocytes. Several recent studies have examined the role of Ca(2+) dynamics in normal podocyte function and their possible contributions to glomerular disease. This review summarizes the properties of TRPC6 and related channels, focusing on their permeation and gating properties, the nature of mutations associated with familial FSGS, and the role of TRPC channels in podocyte cell biology as well as in glomerular pathophysiology. TRPC6 interacts with several proteins in podocytes, including essential slit diaphragm proteins and mechanosensitive large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels. The signaling dynamics controlling ion channel function and localization in podocytes appear to be quite complex.
Figures

References
-
- Beisel KW, Rocha-Sanchez SM, Ziegenbein SJ, Morris KA, Kai C, Kawai J, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Davis RL. Diversity of Ca2+-activated K+ channel transcripts in inner ear hair cells. Gene 386: 11–23, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Boulay G. Ca2+-calmodulin regulates receptor-operated Ca2+ entry activity of TRPC6 in HEK-293 cells. Cell Calcium 32: 201–207, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C. NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24: 349–354, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

