Research resource: Tissue-specific transcriptomics and cistromics of nuclear receptor signaling: a web research resource
- PMID: 20685849
- PMCID: PMC2954640
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0216
Research resource: Tissue-specific transcriptomics and cistromics of nuclear receptor signaling: a web research resource
Abstract
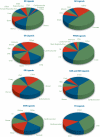
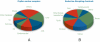
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are ligand-regulated transcription factors that recruit coregulators and other transcription factors to gene promoters to effect regulation of tissue-specific transcriptomes. The prodigious rate at which the NR signaling field has generated high content gene expression and, more recently, genome-wide location analysis datasets has not been matched by a committed effort to archiving this information for routine access by bench and clinical scientists. As a first step towards this goal, we searched the MEDLINE database for studies, which referenced either expression microarray and/or genome-wide location analysis datasets in which a NR or NR ligand was an experimental variable. A total of 1122 studies encompassing 325 unique organs, tissues, primary cells, and cell lines, 35 NRs, and 91 NR ligands were retrieved and annotated. The data were incorporated into a new section of the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas Molecule Pages, Transcriptomics and Cistromics, for which we designed an intuitive, freely accessible user interface to browse the studies. Each study links to an abstract, the MEDLINE record, and, where available, Gene Expression Omnibus and ArrayExpress records. The resource will be updated on a regular basis to provide a current and comprehensive entrez into the sum of transcriptomic and cistromic research in this field.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptomine, a web resource for nuclear receptor signaling transcriptomes.Physiol Genomics. 2012 Sep 1;44(17):853-63. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00033.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Physiol Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22786849 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery-driven research and bioinformatics in nuclear receptor and coregulator signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1812(8):808-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.10.009. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21029773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (www.nursa.org): hyperlinking the nuclear receptor signaling community.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D221-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj029. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381851 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas: Opening Access to the Biology of Nuclear Receptor Signaling Pathways.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 1;10(9):e0135615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135615. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26325041 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Evolution of NURSA, the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jun;23(6):740-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0135. Epub 2009 May 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19423650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomine, a web resource for nuclear receptor signaling transcriptomes.Physiol Genomics. 2012 Sep 1;44(17):853-63. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00033.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Physiol Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22786849 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery-driven research and bioinformatics in nuclear receptor and coregulator signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Aug;1812(8):808-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.10.009. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21029773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheung E, Kraus WL 2010 Genomic analyses of hormone signaling and gene regulation. Annu Rev Physiol 72:191–218 - PubMed
-
- Lupien M, Brown M 2009 Cistromics of hormone-dependent cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 16:381–389 - PubMed
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Ström A, Treuter E, Warner M, Gustafsson JA 2007 Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev 87:905–931 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

