Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor knockout mice are protected from high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance
- PMID: 20685876
- PMCID: PMC2946144
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-0289
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor knockout mice are protected from high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance
Abstract
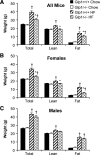
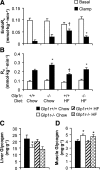
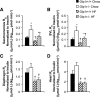
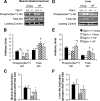
Glucagon-like peptide-1 augments nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion. Chow-fed mice lacking the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (Glp1r) exhibit enhanced insulin-stimulated muscle glucose uptake but impaired suppression of endogenous glucose appearance (endoRa). This proposes a novel role for the Glp1r to regulate the balance of glucose disposal in muscle and liver by modulating insulin action. Whether this is maintained in an insulin-resistant state is unknown. The present studies tested the hypothesis that disruption of Glp1r expression overcomes high-fat (HF) diet-induced muscle insulin resistance and exacerbates HF diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance. Mice with a functional disruption of the Glp1r (Glp1r-/-) were compared with wild-type littermates (Glp1r+/+) after 12 wk on a regular chow diet or a HF diet. Arterial and venous catheters were implanted for sampling and infusions. Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps were performed on weight-matched male mice. [3-(3)H]glucose was used to determine glucose turnover, and 2[14C]deoxyglucose was used to measure the glucose metabolic index, an indicator of glucose uptake. Glp1r-/- mice exhibited increased glucose disappearance and muscle glucose metabolic index on either diet. This was associated with enhanced activation of muscle Akt and AMP-activated protein kinase and reduced muscle triglycerides in HF-fed Glp1r-/- mice. Chow-fed Glp1r-/- mice exhibited impaired suppression of endoRa and hepatic insulin signaling. In contrast, HF-fed Glp1r-/- mice exhibited improved suppression of endoRa and hepatic Akt activation. This was associated with decreased hepatic triglycerides and impaired activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1. These results show that mice lacking the Glp1r are protected from HF diet-induced muscle and hepatic insulin resistance independent of effects on total fat mass.
Figures

References
-
- Campos RV, Lee YC, Drucker DJ 1994 Divergent tissue-specific and developmental expression of receptors for glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 in the mouse. Endocrinology 134:2156–2164 - PubMed
-
- Bullock BP, Heller RS, Habener JF 1996 Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Endocrinology 137:2968–2978 - PubMed
-
- Miyawaki K, Yamada Y, Yano H, Niwa H, Ban N, Ihara Y, Kubota A, Fujimoto S, Kajikawa M, Kuroe A, Tsuda K, Hashimoto H, Yamashita T, Jomori T, Tashiro F, Miyazaki J, Seino Y 1999 Glucose intolerance caused by a defect in the entero-insular axis: a study in gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14843–14847 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Komatsu R, Matsuyama T, Namba M, Watanabe N, Itoh H, Kono N, Tarui S 1989 Glucagonostatic and insulinotropic action of glucagonlike peptide I-(7–36)-amide. Diabetes 38:902–905 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

