Osmoprotective transcription factor NFAT5/TonEBP modulates nuclear factor-kappaB activity
- PMID: 20685965
- PMCID: PMC2947481
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-02-0133
Osmoprotective transcription factor NFAT5/TonEBP modulates nuclear factor-kappaB activity
Abstract
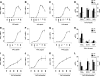
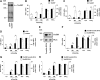
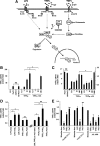
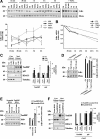
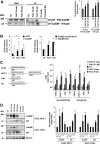
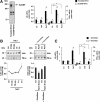
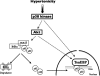
Tonicity-responsive binding-protein (TonEBP or NFAT5) is a widely expressed transcription factor whose activity is regulated by extracellular tonicity. TonEBP plays a key role in osmoprotection by binding to osmotic response element/TonE elements of genes that counteract the deleterious effects of cell shrinkage. Here, we show that in addition to this "classical" stimulation, TonEBP protects cells against hypertonicity by enhancing nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity. We show that hypertonicity enhances NF-κB stimulation by lipopolysaccharide but not tumor necrosis factor-α, and we demonstrate overlapping protein kinase B (Akt)-dependent signal transduction pathways elicited by hypertonicity and transforming growth factor-α. Activation of p38 kinase by hypertonicity and downstream activation of Akt play key roles in TonEBP activity, IκBα degradation, and p65 nuclear translocation. TonEBP affects neither of these latter events and is itself insensitive to NF-κB signaling. Rather, we reveal a tonicity-dependent interaction between TonEBP and p65 and show that NF-κB activity is considerably enhanced after binding of NF-κB-TonEBP complexes to κB elements of NF-κB-responsive genes. We demonstrate the key roles of TonEBP and Akt in renal collecting duct epithelial cells and in macrophages. These findings reveal a novel role for TonEBP and Akt in NF-κB activation on the onset of hypertonic challenge.
Figures


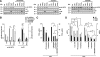
Similar articles
-
Pinitol targets nuclear factor-kappaB activation pathway leading to inhibition of gene products associated with proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and angiogenesis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jun;7(6):1604-14. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2424. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18566231
-
NF-κB is activated in response to temozolomide in an AKT-dependent manner and confers protection against the growth suppressive effect of the drug.J Transl Med. 2012 Dec 21;10:252. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-252. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 23259744 Free PMC article.
-
Neurokinin A engages neurokinin-1 receptor to induce NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression in murine macrophages: implications of ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/Akt pathways.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):C679-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00042.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18596216
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Tonicity-independent regulation of the osmosensitive transcription factor TonEBP (NFAT5).Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Jan 1;302(1):C1-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00327.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21998140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Inhibition of NFAT5-Mediated Induction of CCL2 in Hyperosmotic Conditions by Cyclosporine and Dexamethasone on Human HeLa-Modified Conjunctiva-Derived Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 3;11(8):e0159983. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159983. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27486749 Free PMC article.
-
Alternations of NF-κB Signaling by Natural Compounds in Muscle-Derived Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 25;24(15):11900. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511900. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do kinases contribute to tonicity-dependent regulation of the transcription factor NFAT5?World J Nephrol. 2016 Jan 6;5(1):20-32. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i1.20. World J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26788461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequential and synchronized hypertonicity-induced activation of Rel-family transcription factors is required for osmoprotection in renal cells.Heliyon. 2018 Dec 21;4(12):e01072. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e01072. eCollection 2018 Dec. Heliyon. 2018. PMID: 30603705 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation with the Aureobasidium pullulans-produced β-glucan effectively induces interferon stimulated genes in macrophage-like cell lines.Sci Rep. 2014 Apr 24;4:4777. doi: 10.1038/srep04777. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24759061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrieu N., Salvayre R., Jaffrezou J. P., Levade T. Low temperatures and hypertonicity do not block cytokine-induced stimulation of the sphingomyelin pathway but inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:24518–24524. - PubMed
-
- Biswas D. K., Iglehart J. D. Linkage between EGFR family receptors and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling in breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006;209:645–652. - PubMed
-
- Burg M., Ferraris J., Dmitrieva N. Cellular response to hypertonic stress. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87:1441–1474. - PubMed
-
- Canono B. P., Campbell P. A. Production of mouse inflammatory macrophage hybridomas. J. Tissue Cult. Methods. 1992;14:3–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

