Fragile X mental retardation protein is required for rapid experience-dependent regulation of the potassium channel Kv3.1b
- PMID: 20685971
- PMCID: PMC3485078
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1125-10.2010
Fragile X mental retardation protein is required for rapid experience-dependent regulation of the potassium channel Kv3.1b
Abstract
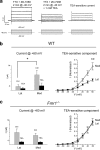
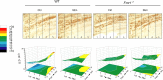
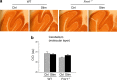
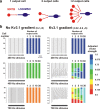
Fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) is an RNA-binding protein that regulates synaptic plasticity by repressing translation of specific mRNAs. We found that FMRP binds mRNA encoding the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv3.1b in brainstem synaptosomes. To explore the regulation of Kv3.1b by FMRP, we investigated Kv3.1b immunoreactivity and potassium currents in the auditory brainstem sound localization circuit of male mice. The unique features of this circuit allowed us to control neuronal activity in vivo by exposing animals to high-frequency, amplitude-modulated stimuli, which elicit predictable and stereotyped patterns of input to the anterior ventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB). In wild-type (WT) animals, Kv3.1b is expressed along a tonotopic gradient in the MNTB, with highest levels in neurons at the medial, high-frequency end. At baseline, Fmr1(-/-) mice, which lack FMRP, displayed dramatically flattened tonotopicity in Kv3.1b immunoreactivity and K(+) currents relative to WT controls. Moreover, after 30 min of acoustic stimulation, levels of Kv3.1b immunoreactivity were significantly elevated in both the MNTB and AVCN of WT, but not Fmr1(-/-), mice. These results suggest that FMRP is necessary for maintenance of the gradient in Kv3.1b protein levels across the tonotopic axis of the MNTB, and are consistent with a role for FMRP as a repressor of protein translation. Using numerical simulations, we demonstrate that Kv3.1b tonotopicity may be required for accurate encoding of stimulus features such as modulation rate, and that disruption of this gradient, as occurs in Fmr1(-/-) animals, degrades processing of this information.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Modulators of Kv3 Potassium Channels Rescue the Auditory Function of Fragile X Mice.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 12;39(24):4797-4813. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0839-18.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 1. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30936239 Free PMC article.
-
Specific and rapid effects of acoustic stimulation on the tonotopic distribution of Kv3.1b potassium channels in the adult rat.Neuroscience. 2010 May 19;167(3):567-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.046. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20219640 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of fragile X mental retardation protein in the human auditory brainstem.Neuroscience. 2014 Jul 25;273:79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 May 15. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24838064
-
Potassium channel modulation and auditory processing.Hear Res. 2011 Sep;279(1-2):32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21414395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the timing of MNTB neurons by short-term and long-term modulation of potassium channels.Hear Res. 2005 Aug;206(1-2):133-45. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2004.11.023. Hear Res. 2005. PMID: 16081004 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of Fmr1 alters function and synaptic inputs in the auditory brainstem.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0117266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117266. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25679778 Free PMC article.
-
Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein Restricts Small Dye Iontophoresis Entry into Central Neurons.J Neurosci. 2017 Oct 11;37(41):9844-9858. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0723-17.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 8. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28887386 Free PMC article.
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein and synaptic plasticity.Mol Brain. 2013 Apr 8;6:15. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-6-15. Mol Brain. 2013. PMID: 23566911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tsc1 represses parvalbumin expression and fast-spiking properties in somatostatin lineage cortical interneurons.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 1;10(1):4994. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12962-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31676823 Free PMC article.
-
From FMRP function to potential therapies for fragile X syndrome.Neurochem Res. 2014 Jun;39(6):1016-31. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1229-3. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24346713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashley CT, Jr, Wilkinson KD, Reines D, Warren ST. FMR1 protein: conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science. 1993;262:563–566. - PubMed
-
- Baranauskas G, Tkatch T, Nagata K, Yeh JZ, Surmeier DJ. Kv3.4 subunits enhance the repolarizing efficiency of Kv3.1 channels in fast-spiking neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:258–266. - PubMed
-
- Brew HM, Forsythe ID. Systematic variation of potassium current amplitudes across the tonotopic axis of the rat medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Hear Res. 2005;206:116–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
