Basolateral amygdala cdk5 activity mediates consolidation and reconsolidation of memories for cocaine cues
- PMID: 20685978
- PMCID: PMC3150196
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2112-10.2010
Basolateral amygdala cdk5 activity mediates consolidation and reconsolidation of memories for cocaine cues
Abstract
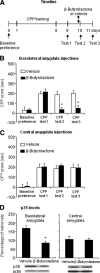
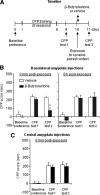
Cocaine use and relapse involves learned associations between cocaine-associated environmental contexts and discrete stimuli and cocaine effects. Initially, these contextual and discrete cues undergo memory consolidation after being paired with cocaine exposure. During abstinence, cocaine cue memories can undergo memory reconsolidation after cue exposure without the drug. We used a conditioned place preference (CPP) procedure in rats to study the role of neuronal protein kinase cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) in consolidation and reconsolidation of cocaine cue memories. We found that the expression of cocaine CPP in drug-free tests 1 d after CPP training (four pairings of 10 mg/kg cocaine with one context and four pairings of saline with a different context) increased Cdk5 activity, and levels of the Cdk5 activator p35 in basolateral but not central amygdala. We also found that basolateral (but not central) amygdala injections of the Cdk5 inhibitor beta-butyrolactone (100 ng/side) immediately (but not 6 h) after cocaine-context pairings during training prevented subsequent cocaine CPP expression. After training, acute basolateral (but not central) amygdala beta-butyrolactone injections immediately before testing prevented the expression of cocaine CPP; this effect was also observed on a second test performed 1 d later, suggesting an effect on reconsolidation of cocaine cue memories. In support, basolateral beta-butyrolactone injections, given immediately (but not 6 h) after a single exposure to the cocaine-paired context, prevented cocaine CPP expression 1 and 14 d after the injections. Results indicate that basolateral amygdala Cdk5 activity is critical for consolidation and reconsolidation of the memories of cocaine-associated environmental cues.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β in the basolateral amygdala is critical for the reconsolidation of cocaine reward memory.J Neurochem. 2011 Jul;118(1):113-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07277.x. Epub 2011 May 19. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21592120
-
Region-specific role of Rac in nucleus accumbens core and basolateral amygdala in consolidation and reconsolidation of cocaine-associated cue memory in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Aug;228(3):427-37. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3050-8. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23494234
-
eIF2α dephosphorylation in basolateral amygdala mediates reconsolidation of drug memory.J Neurosci. 2014 Jul 23;34(30):10010-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0934-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25057203 Free PMC article.
-
Neural substrates of cocaine-cue associations that trigger relapse.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 5;526(1-3):140-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.034. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16253228 Review.
-
The psychological and neurochemical mechanisms of drug memory reconsolidation: implications for the treatment of addiction.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Jun;31(12):2308-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07249.x. Epub 2010 May 24. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20497475 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of hippocampal β-adrenergic and glucocorticoid receptors in the novelty-induced enhancement of fear extinction.J Neurosci. 2015 May 27;35(21):8308-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0005-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26019344 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of calpain/p35-p25/Cdk5/NMDAR signaling pathway in glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat retinal neurons.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42318. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042318. Epub 2012 Aug 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22870316 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IKK/NF-κB signaling in extinction of conditioned place aversion memory in rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039696. Epub 2012 Jun 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761874 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsolidation of a cocaine associated memory requires DNA methyltransferase activity in the basolateral amygdala.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 20;5:13327. doi: 10.1038/srep13327. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26289919 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine place conditioning increases pro-opiomelanocortin gene expression in rat hypothalamus.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Nov 14;530(1):59-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.09.060. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 23069669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Benavides DR, Bibb JA. Role of Cdk5 in drug abuse and plasticity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1025:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Beninger RJ, Gerdjikov T. The role of signaling molecules in reward-related incentive learning. Neurotox Res. 2004;6:91–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
