Ca(v)3.2 T-type Ca2+ channel-dependent activation of ERK in paraventricular thalamus modulates acid-induced chronic muscle pain
- PMID: 20685979
- PMCID: PMC6634662
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1041-10.2010
Ca(v)3.2 T-type Ca2+ channel-dependent activation of ERK in paraventricular thalamus modulates acid-induced chronic muscle pain
Abstract
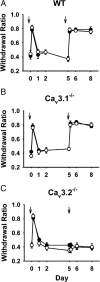
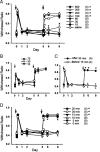
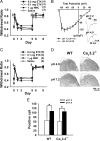
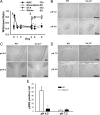
Treatments for chronic musculoskeletal pain, such as lower back pain, fibromyalgia, and myofascial pain syndrome, remain inadequate because of our poor understanding of the mechanisms that underlie these conditions. Although T-type Ca2+ channels (T-channels) have been implicated in peripheral and central pain sensory pathways, their role in chronic musculoskeletal pain is still unclear. Here, we show that acid-induced chronic mechanical hyperalgesia develops in Ca(v)3.1-deficient and wild-type but not in Ca(v)3.2-deficient male and female mice. We also show that T-channels are required for the initiation, but not maintenance, of acid-induced chronic muscle pain. Blocking T-channels using ethosuximide prevented chronic mechanical hyperalgesia in wild-type mice when administered intraperitoneally or intracerebroventricularly, but not intramuscularly or intrathecally. Furthermore, we found an acid-induced, Ca(v)3.2 T-channel-dependent activation of ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) in the anterior nucleus of paraventricular thalamus (PVA), and prevention of the ERK activation abolished the chronic mechanical hyperalgesia. Our findings suggest that Ca(v)3.2 T-channel-dependent activation of ERK in PVA is required for the development of acid-induced chronic mechanical hyperalgesia.
Figures
References
-
- Altier C, Zamponi GW. Targeting Ca2+ channels to treat pain: T-type versus N-type. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:465–470. - PubMed
-
- Bernard JF, Peschanski M, Besson JM. A possible spino (trigemino)-ponto-amygdaloid pathway for pain. Neurosci Lett. 1989;100:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Bhave G, Karim F, Carlton SM, Gereau RW., 4th Peripheral group I metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate nociception in mice. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:417–423. - PubMed
-
- Bullitt E. Expression of c-fos-like protein as a marker for neuronal activity following noxious stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990;296:517–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
