Attentional facilitation throughout human visual cortex lingers in retinotopic coordinates after eye movements
- PMID: 20685992
- PMCID: PMC2925081
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1546-10.2010
Attentional facilitation throughout human visual cortex lingers in retinotopic coordinates after eye movements
Abstract
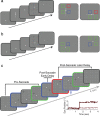
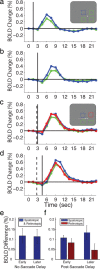
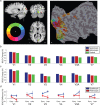
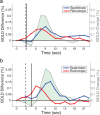
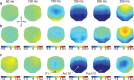
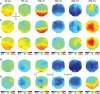
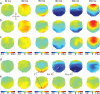
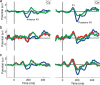
With each eye movement, the image of the world received by the visual system changes dramatically. To maintain stable spatiotopic (world-centered) visual representations, the retinotopic (eye-centered) coordinates of visual stimuli are continually remapped, even before the eye movement is completed. Recent psychophysical work has suggested that updating of attended locations occurs as well, although on a slower timescale, such that sustained attention lingers in retinotopic coordinates for several hundred milliseconds after each saccade. To explore where and when this "retinotopic attentional trace" resides in the cortical visual processing hierarchy, we conducted complementary functional magnetic resonance imaging and event-related potential (ERP) experiments using a novel gaze-contingent task. Human subjects executed visually guided saccades while covertly monitoring a fixed spatiotopic target location. Although subjects responded only to stimuli appearing at the attended spatiotopic location, blood oxygen level-dependent responses to stimuli appearing after the eye movement at the previously, but no longer, attended retinotopic location were enhanced in visual cortical area V4 and throughout visual cortex. This retinotopic attentional trace was also detectable with higher temporal resolution in the anterior N1 component of the ERP data, a well established signature of attentional modulation. Together, these results demonstrate that, when top-down spatiotopic signals act to redirect visuospatial attention to new retinotopic locations after eye movements, facilitation transiently persists in the cortical regions representing the previously relevant retinotopic location.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen RA, Snyder LH, Bradley DC, Xing J. Multimodal representation of space in the posterior parietal cortex and its use in planning movements. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:303–330. - PubMed
-
- Awh E, Anllo-Vento L, Hillyard SA. The role of spatial selective attention in working memory for locations: evidence from event-related potentials. J Cogn Neurosci. 2000;12:840–847. - PubMed
-
- Brainard DH. The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis. 1997;10:433–436. - PubMed
-
- Bridgeman B, Van der Heijden AHC, Velichkovsky BM. A theory of visual stability across saccadic eye movements. Behav Brain Sci. 1994;17:247–257.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
