Properties of the Arg376 residue of the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) and a glutamine mutant causing hereditary folate malabsorption
- PMID: 20686069
- PMCID: PMC2980313
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00113.2010
Properties of the Arg376 residue of the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) and a glutamine mutant causing hereditary folate malabsorption
Abstract
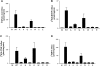
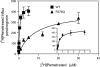
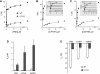
The proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) is required for intestinal folate absorption and is mutated in the autosomal recessive disorder, hereditary folate malabsorption (HFM). This report characterizes properties and requirements of the R376 residue in PCFT function, including a R376Q mutant associated with HFM. Gln, Cys, and Ala substitutions resulted in markedly impaired transport of 5-formyltetrahydrofolate (5-FTHF) and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) due to an increase in K(m) and decrease in V(max) in HeLa R1-11 transfectants lacking endogenous folate transport function. In contrast, although the influx K(m) for pemetrexed was increased, transport was fully preserved at saturating concentrations and enhanced for the like-charged R376K- and R376H-PCFT. Pemetrexed and 5-FTHF influx mediated by R376Q-PCFT was markedly decreased at pH 5.5 compared with wild-type PCFT. However, while pemetrexed transport was substantially preserved at low pH (4.5-5.0), 5-FTHF transport remained very low. Electrophysiological studies in Xenopus oocytes demonstrated that 1) the R376Q mutant, like wild-type PCFT, transports protons in the absence of folate substrate, and in this respect has channel-like properties; and 2) the influx K(m) mediated by R376Q-PCFT is increased for 5-MTHF, 5-FTHF, and pemetrexed. The data suggest that mutation of the R376 residue to Gln impairs proton binding which, in turn, modulates the folate-binding pocket and depresses the rate of conformational alteration of the carrier, a change that appears to be, in part, substrate dependent.
Figures

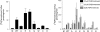
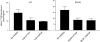
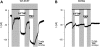
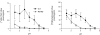
Similar articles
-
Functional roles of the A335 and G338 residues of the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) mutated in hereditary folate malabsorption.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):C834-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00171.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22843796 Free PMC article.
-
A P425R mutation of the proton-coupled folate transporter causing hereditary folate malabsorption produces a highly selective alteration in folate binding.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012 May 1;302(9):C1405-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00435.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22345511 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Tyr residues that enhance folate substrate binding and constrain oscillation of the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1).Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Apr 15;308(8):C631-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00238.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25608532 Free PMC article.
-
The proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) and the syndrome of systemic and cerebral folate deficiency of infancy: Hereditary folate malabsorption.Mol Aspects Med. 2017 Feb;53:57-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Mol Aspects Med. 2017. PMID: 27664775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human proton-coupled folate transporter: Biology and therapeutic applications to cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Dec;13(14):1355-73. doi: 10.4161/cbt.22020. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22954694 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the tryptophan residues in proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) function.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):C150-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00084.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27251438 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of aspartate residues of the proton-coupled folate transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1); a D156Y mutation causing hereditary folate malabsorption.Blood. 2010 Dec 9;116(24):5162-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-291237. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20805364 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an Extracellular Gate for the Proton-coupled Folate Transporter (PCFT-SLC46A1) by Cysteine Cross-linking.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 8;291(15):8162-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693929. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26884338 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving biology of the proton-coupled folate transporter: New insights into regulation, structure, and mechanism.FASEB J. 2022 Feb;36(2):e22164. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101704R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35061292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of a loss-of-function mutation in the proton-coupled folate transporter gene (PCFT-SLC46A1) causing hereditary folate malabsorption in Puerto Rico.J Pediatr. 2011 Oct;159(4):623-7.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.03.005. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 21489556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cario H, Bode H, Debatin KM, Opladen T, Schwarz K. Congenital null mutations of the FOLR1 gene: a progressive neurologic disease and its treatment. Neurology 73: 2127–2129, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay S, Moran RG, Goldman ID. Pemetrexed: biochemical and cellular pharmacology, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 404–417, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

