Global phosphorylation analysis of beta-arrestin-mediated signaling downstream of a seven transmembrane receptor (7TMR)
- PMID: 20686112
- PMCID: PMC2930550
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1008461107
Global phosphorylation analysis of beta-arrestin-mediated signaling downstream of a seven transmembrane receptor (7TMR)
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 14;109(33):13464
Abstract
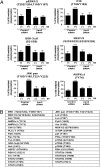
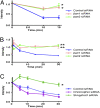
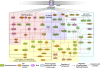
beta-Arrestin-mediated signaling downstream of seven transmembrane receptors (7TMRs) is a relatively new paradigm for signaling by these receptors. We examined changes in protein phosphorylation occurring when HEK293 cells expressing the angiotensin II type 1A receptor (AT1aR) were stimulated with the beta-arrestin-biased ligand Sar(1), Ile(4), Ile(8)-angiotensin (SII), a ligand previously found to signal through beta-arrestin-dependent, G protein-independent mechanisms. Using a phospho-antibody array containing 46 antibodies against signaling molecules, we found that phosphorylation of 35 proteins increased upon SII stimulation. These SII-mediated phosphorylation events were abrogated after depletion of beta-arrestin 2 through siRNA-mediated knockdown. We also performed an MS-based quantitative phosphoproteome analysis after SII stimulation using a strategy of stable isotope labeling of amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). We identified 1,555 phosphoproteins (4,552 unique phosphopeptides), of which 171 proteins (222 phosphopeptides) showed increased phosphorylation, and 53 (66 phosphopeptides) showed decreased phosphorylation upon SII stimulation of the AT1aR. This study identified 38 protein kinases and three phosphatases whose phosphorylation status changed upon SII treatment. Using computational approaches, we performed system-based analyses examining the beta-arrestin-mediated phosphoproteome including construction of a kinase-substrate network for beta-arrestin-mediated AT1aR signaling. Our analysis demonstrates that beta-arrestin-dependent signaling processes are more diverse than previously appreciated. Notably, our analysis identifies an AT1aR-mediated cytoskeletal reorganization network whereby beta-arrestin regulates phosphorylation of several key proteins, including cofilin and slingshot. This study provides a system-based view of beta-arrestin-mediated phosphorylation events downstream of a 7TMR and opens avenues for research in a rapidly evolving area of 7TMR signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:639–650. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science. 2005;308:512–517. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Whalen EJ. Beta-arrestins: Traffic cops of cell signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Olsen JV, et al. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell. 2006;127:635–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 GM071558/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL16037/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HG3456/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL016037/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070631/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067945/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003456/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- GM67945/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DK088541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM071558-01A27398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL70631/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

