Family history of Alzheimer's disease and hippocampal structure in healthy people
- PMID: 20686185
- PMCID: PMC3086166
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.09111575
Family history of Alzheimer's disease and hippocampal structure in healthy people
Abstract
Objective: Structural brain changes appear years before the onset of Alzheimer's disease, the leading cause of dementia late in life. Determining risk factors for such presymptomatic brain changes may assist in identifying candidates for future prevention treatment trials. In addition to the e4 allele of the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE-4), the major known genetic risk factor, a family history of Alzheimer's disease also increases the risk to develop the disease, reflecting yet unidentified genetic and, perhaps, nongenetic risks. The authors investigated the influence of APOE-4 genotype and family history risks on cortical thickness in medial temporal lobe subregions among volunteers without cognitive impairment.
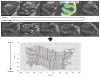
Method: High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and a cortical unfolding method were performed on 26 subjects (APOE-4 carriers: N=13; noncarriers: N=13) with at least one first-degree relative with Alzheimer's disease and 25 subjects (APOE-4 carriers: N=12; noncarriers: N=13) without this risk factor. All subjects (mean age: 62.3 years [SD=10.7]; range=38-86 years) were cognitively healthy.
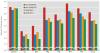
Results: Family history of Alzheimer's disease and APOE-4 status were associated with a thinner cortex in the entorhinal region, subiculum, and adjacent medial temporal lobe subfields. Although these associations were additive, family history of Alzheimer's disease explained a greater proportion of the unique variance in cortical thickness than APOE-4 carrier status.
Conclusions: APOE-4 carrier status and family history of Alzheimer's disease are independently associated with and contribute additively to hippocampal cortical thinning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Psychiatry Res. 2013 Dec 30;214(3):212-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Psychiatry Res. 2013. PMID: 24080518 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal changes in medial temporal cortical thickness in normal subjects with the APOE-4 polymorphism.Neuroimage. 2010 Oct 15;53(1):37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.009. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20541611 Free PMC article.
-
Major decrease in the volume of the entorhinal cortex in patients with Alzheimer's disease carrying the apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998 Sep;65(3):322-7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.65.3.322. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998. PMID: 9728943 Free PMC article.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging studies and APOE genotype in persons at risk for Alzheimer's disease.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2006 Feb;8(1):11-7. doi: 10.1007/s11920-006-0076-1. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2006. PMID: 16513038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The presymptomatic phase of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: are we merely scratching the surface?J Neurol. 2021 Dec;268(12):4607-4629. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10289-5. Epub 2020 Oct 31. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33130950
-
Cognitive Functioning of Unaffected First-degree Relatives of Individuals With Late-onset Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis.Neuropsychol Rev. 2023 Dec;33(4):659-674. doi: 10.1007/s11065-022-09555-2. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Neuropsychol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36057684 Free PMC article.
-
Young Adults with a Parent with Dementia Show Early Abnormalities in Brain Activity and Brain Volume in the Hippocampus: A Matched Case-Control Study.Brain Sci. 2022 Apr 13;12(4):496. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12040496. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35448026 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein ε4 modifies obesity-related atrophy in the hippocampal formation of cognitively healthy adults.Neurobiol Aging. 2022 May;113:39-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Neurobiol Aging. 2022. PMID: 35303671 Free PMC article.
-
Low Subicular Volume as an Indicator of Dementia-Risk Susceptibility in Old Age.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 3;14:811146. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.811146. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35309894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mount C, Downton C. Alzheimer disease: progress or profit? Nat Med. 2006;12:780–784. - PubMed
-
- Brouwers N, Sleegers K, Van Broeckhoven C. Molecular genetics of Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Ann Med. 2008;40:562–583. - PubMed
-
- Shaw P, Lerch JP, Pruessner JC, Taylor KN, Rose AB, Greenstein D, Clasen L, Evans A, Rapoport JL, Giedd JN. Cortical morphology in children and adolescents with different apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms: an observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:494–500. - PubMed
-
- Cupples LA, Farrer LA, Sadovnick AD, Relkin N, Whitehouse P, Green RC. Estimating risk curves for first-degree relatives of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: the REVEAL Study. Genet Med. 2004;6:192–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

