The NOSE study (nasal ointment for Staphylococcus aureus eradication): a randomized controlled trial of monthly mupirocin in HIV-infected individuals
- PMID: 20686410
- PMCID: PMC2974816
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181ec2a68
The NOSE study (nasal ointment for Staphylococcus aureus eradication): a randomized controlled trial of monthly mupirocin in HIV-infected individuals
Abstract
Background: HIV-positive patients at HELP/PSI, Inc, an in-patient drug rehabilitation center, had a high baseline prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus colonization (49%) and incidence of infection (17%) in a previous year-long study.
Methods: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted to determine whether repeated nasal application of mupirocin ointment would decrease the odds of S. aureus nasal colonization in 100 HELP/PSI patients over an 8-month period. A 5-day course of study drug was given monthly, and colonization was assessed at baseline and 1 month after each treatment. S. aureus infection was a secondary outcome.
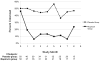
Results: In repeated-measures analysis, mupirocin reduced the odds of monthly S. aureus nasal colonization by 83% compared with placebo [adjusted odds ratio (ORadj) = 0.17; P < 0.0001]. Subjects colonized at study entry had a 91% reduction in subsequent colonization (ORadj = 0.09; P < 0.0001). Mupirocin also suppressed S. aureus colonization in subjects not colonized at baseline (ORadj = 0.23; P = 0.006). There was no difference in infection rates between the mupirocin and placebo groups (hazard ratio = 0.49, P = 0.29).
Conclusions: Monthly application of nasal mupirocin significantly decreased S. aureus colonization in HIV patients in residential drug rehabilitation. Monthly mupirocin application has a potential role in long-term care settings or in HIV-positive patients with high rates of S. aureus colonization and infection.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors report any conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998 Aug 20;339(8):520–532. - PubMed
-
- Wertheim HF, Melles DC, Vos MC, et al. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005 Dec;5(12):751– 762. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen MH, Kauffman CA, Goodman RP, et al. Nasal carriage of and infection with Staphylococcus aureus in HIV-infected patients. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Feb 2;130(3):221–225. - PubMed
-
- Miller M, Cespedes C, Vavagiakis P, Klein RS, Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus colonization in a community sample of HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected drug users. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003 Aug;22(8):463–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

