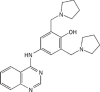
State-dependent blockade of human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) K(+) channels by changrolin in stably transfected HEK293 cells
- PMID: 20686516
- PMCID: PMC4007811
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.84
State-dependent blockade of human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) K(+) channels by changrolin in stably transfected HEK293 cells
Abstract
Aim: To study the effect of changrolin on the K(+) channels encoded by the human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG).
Methods: hERG channels were heterologously stably expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells, and the hERG K(+) currents were recorded using a standard whole-cell patch-clamp technique.
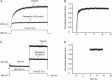
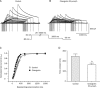
Results: Changrolin inhibited hERG channels in a concentration-dependent and reversible manner (IC(50)=18.23 mumol/L, 95% CI: 9.27-35.9 mumol/L; Hill coefficient=-0.9446). In addition, changrolin shifted the activation curve of hERG channels by 14.3+/-1.5 mV to more negative potentials (P<0.01, n=9) but did not significantly affect the steady-state inactivation of hERG (n=5, P>0.05). The relative block of hERG channels by changrolin was close to zero at the time point of channel opening by the depolarizing voltage step and quickly increased afterwards. The maximal block was achieved in the inactivated state, with no further development of the open channel block. In the "envelope of tails" experiments, the time constants of activation were found to be 287.8+/-46.2 ms and 174.2+/-18.4 ms, respectively, for the absence and presence of 30 mumol/L changrolin (P<0.05, n=7). The onset of inactivation was accelerated significantly by changrolin between -40 mV and +60 mV (P<0.05, n=7).
Conclusion: The results demonstrate that changrolin is a potent hERG blocker that preferentially binds to hERG channels in the open and inactivated states.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Block of HERG current expressed in HEK293 cells by the Na+-channel blocker cibenzoline.Heart Vessels. 2004 May;19(3):137-43. doi: 10.1007/s00380-003-0750-8. Heart Vessels. 2004. PMID: 15168062
-
Characteristics of hERG and hNav1.5 channel blockade by sulcardine sulfate, a novel anti-arrhythmic compound.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 5;844:130-138. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.12.009. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30529471
-
Inhibition of the HERG channel by droperidol depends on channel gating and involves the S6 residue F656.Anesth Analg. 2008 Apr;106(4):1161-70, table of contents. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e3181684974. Anesth Analg. 2008. Retraction in: Anesth Analg. 2008 Sep;107(3):1040. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31817e7b40. PMID: 18349188 Retracted.
-
Blockade of the human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel by ketanserin.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Aug 25;60(4):525-34. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18690396
-
Eag and HERG potassium channels as novel therapeutic targets in cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2010 Dec 29;8:113. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-8-113. World J Surg Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21190577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-6 inhibition of hERG underlies risk for acquired long QT in cardiac and systemic inflammation.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 6;13(12):e0208321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208321. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30521586 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products modulating the hERG channel: heartaches and hope.Nat Prod Rep. 2017 Aug 2;34(8):957-980. doi: 10.1039/c7np00014f. Nat Prod Rep. 2017. PMID: 28497823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Preclinical Pharmacokinetic Properties and Prediction of Human PK Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for a Novel Anti-Arrhythmic Agent Sulcardine Sulfate.Pharm Res. 2021 Nov;38(11):1847-1862. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03128-3. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Pharm Res. 2021. Retraction in: Pharm Res. 2023 May;40(5):1311. doi: 10.1007/s11095-023-03489-x. PMID: 34773182 Retracted.
-
Oral Bioavailability and Mass Balance Studies of a Novel Anti-arrhythmic Agent Sulcardine Sulfate in Sprague-Dawley Rats and Beagle Dogs.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017 Jun;42(3):453-459. doi: 10.1007/s13318-016-0360-3. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017. PMID: 27402487
References
-
- Sanguinetti MC, Tristani-Firouzi M. hERG potassium channels and cardiac arrhythmia. Nature. 2006;440:463–9. - PubMed
-
- Hancox JC, McPate MJ, El Harchi A, Zhang YH. The hERG potassium channel and hERG screening for drug-induced torsades de pointes. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;119:118–32. - PubMed
-
- Liu QY, Chen WZ, Wei PJ, Gu PK, Jin ZJ.[Electrophysiological effects of changrolin on single ventricular myocytes isolated from adult guinea pig] Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 198910526–9.Chinese. - PubMed
-
- Shen YT, Xu NS, Gu SL, Wu PM.[Effects of intravenous infusion of changrolin on cardiac function of patients with arrhythmia] Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 19834251–3.Chinese. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

