Discovery of novel PTP1B inhibitors with antihyperglycemic activity
- PMID: 20686525
- PMCID: PMC4007815
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.81
Discovery of novel PTP1B inhibitors with antihyperglycemic activity
Abstract
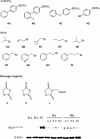
Aim: To discover and optimize a series of novel PTP1B inhibitors containing a thiazolidinone-substituted biphenyl scaffold and to further evaluate the inhibitory effects of these compounds in vitro and in vivo.
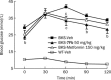
Methods: A total of 36 thiazolidinone substituted biphenyl scaffold derivatives were prepared. An in vitro biological evaluation was done by Enzyme-based assay. The in vivo efficacy of 7Fb as an antihyperglycemic agent was evaluated in a BKS db/db diabetic mouse model with a dose of 50 mg.kg(-1).d(-1) for 4 weeks.
Results: The in vitro biological evaluation showed that compounds 7Fb and 7Fc could increase the insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IRbeta in CHO/hIR cells. In in vivo experiments, compound 7Fb significantly lowered the postprandial blood glucose, from 29.4+/-1.2 mmol/L with the vehicle to 24.7+/-0.6 mmol/L (P<0.01), and the fasting blood glucose from 27.3+/-1.5 mmol/L with the vehicle to 23.6+/-1.2 mmol/L (P<0.05).
Conclusion: A novel series of compounds were discovered to be PTP1B inhibitors. Among them, compound 7Fb significantly lowered the postprandial and fasting glucose levels, and the blood glucose level declined more rapidly than in metformin-treated mice. Thus, 7Fb may be a potential lead compound for developing new agents for the treatment of type II diabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Hunter T. Signaling — 2000 and Beyond. Cell. 2000;100:113–27. - PubMed
-
- Tonks NK, Neel BG. Combinatorial control of the specificity of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:182–95. - PubMed
-
- Kappert K, Peters KG, Bohmer FD, Ostman A. Tyrosine phosphatases in vessel wall signaling. Cardio Vasc Res. 2005;65:587–98. - PubMed
-
- Stoker AW. Protein tyrosine phosphatases and signaling. J Endocrinol. 2005;185:19–33. - PubMed
-
- Tonks NK. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: from genes, to function, to disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2006;7:833–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

