Methicillin resistance transfer from Staphylocccus epidermidis to methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in a patient during antibiotic therapy
- PMID: 20686601
- PMCID: PMC2912275
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011841
Methicillin resistance transfer from Staphylocccus epidermidis to methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in a patient during antibiotic therapy
Abstract
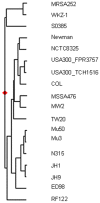
Background: The mecA gene, encoding methicillin resistance in staphylococci, is located on a mobile genetic element called Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec (SCCmec). Horizontal, interspecies transfer of this element could be an important factor in the dissemination of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Previously, we reported the isolation of a closely related methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), MRSA and potential SCCmec donor Staphylococcus epidermidis isolate from the same patient. Based on fingerprint techniques we hypothesized that the S. epidermidis had transferred SCCmec to the MSSA to become MRSA. The aim of this study was to show that these isolates form an isogenic pair and that interspecies horizontal SCCmec transfer occurred.
Methodology/results: Whole genome sequencing of both isolates was performed and for the MSSA gaps were closed by conventional sequencing. The SCCmec of the S. epidermidis was also sequenced by conventional methods. The results show no difference in nucleotide sequence between the two isolates except for the presence of SCCmec in the MRSA. The SCCmec of the S. epidermidis and the MRSA are identical except for a single nucleotide in the ccrB gene, which results in a valine to alanine substitution. The main difference with the closely related EMRSA-16 is the presence of SaPI2 encoding toxic shock syndrome toxin and exfoliative toxin A in the MSSA-MRSA pair. No transfer of SCCmec from the S. epidermidis to the MSSA could be demonstrated in vitro.
Conclusion: The MSSA and MRSA form an isogenic pair except for SCCmec. This strongly supports our hypothesis that the MRSA was derived from the MSSA by interspecies horizontal transfer of SCCmec from S. epidermidis O7.1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Leverstein-van Hall MA, Box ATA, Blok HEM, Paauw A, Fluit AC, et al. Evidence of extensive interspecies transfer of integron-mediated antimicrobial resistance genes among multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in a clinical setting. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Berglund C, Söderquist B. The origin of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate at a neonatal ward in Sweden-possible horizontal transfer of a staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec between methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14:1048–1056. - PubMed
-
- Wielders CL, Vriens MR, Brisse S, de Graaf-Miltenburg LA, Troelstra A, et al. In-vivo transfer of mecA DNA to Staphylococcus aureus corrected]. Lancet. 2001;357:1674–1675. Erratum in: Lancet 2001;358: 424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

