Calycosin promotes angiogenesis involving estrogen receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in zebrafish and HUVEC
- PMID: 20686605
- PMCID: PMC2912279
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011822
Calycosin promotes angiogenesis involving estrogen receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in zebrafish and HUVEC
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis plays an important role in a wide range of physiological processes, and many diseases are associated with the dysregulation of angiogenesis. Radix Astragali is a Chinese medicinal herb commonly used for treating cardiovascular disorders and has been shown to possess angiogenic effect in previous studies but its active constituent and underlying mechanism remain unclear. The present study investigates the angiogenic effects of calycosin, a major isoflavonoid isolated from Radix Astragali, in vitro and in vivo.
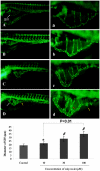
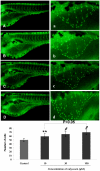
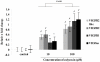
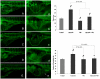
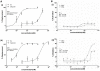
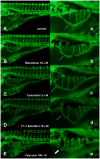
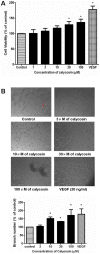
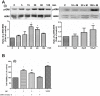
Methodology: Tg(fli1:EGFP) and Tg(fli1:nEGFP) transgenic zebrafish embryos were treated with different concentrations of calycosin (10, 30, 100 microM) from 72 hpf to 96 hpf prior morphological observation and angiogenesis phenotypes assessment. Zebrafish embryos were exposed to calycosin (10, 100 microM) from 72 hpf to 78 hpf before gene-expression analysis. The effects of VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor on calycosin-induced angiogenesis were studied using 72 hpf Tg(fli1:EGFP) and Tg(fli1:nEGFP) zebrafish embryos. The pro-angiogenic effects of calycosin were compared with raloxifene and tamoxifen in 72 hpf Tg(fli1:EGFP) zebrafish embryos. The binding affinities of calycosin to estrogen receptors (ERs) were evaluated by cell-free and cell-based estrogen receptor binding assays. Human umbilical vein endothelial cell cultures (HUVEC) were pretreated with different concentrations of calycosin (3, 10, 30, 100 microM) for 48 h then tested for cell viability and tube formation. The role of MAPK signaling in calycosin-induced angiogenesis was evaluated using western blotting.
Conclusion: Calycosin was shown to induce angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cell cultures (HUVEC) in vitro and zebrafish embryos in vivo via the up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 mRNA expression. It was demonstrated that calycosin acted similar to other selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), such as raloxifene and tamoxifen, by displaying selective potency and affinity to estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta. Our results further indicated that calycosin promotes angiogenesis via activation of MAPK with the involvement of ERK1/2 and ER. Together, this study revealed, for the first time, that calycosin acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) to promote angiogenesis, at least in part through VEGF-VEGFR2 and MAPK signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quercetin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (QODG) inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing VEGFR2-mediated signaling in zebrafish and endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031708. Epub 2012 Feb 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22348123 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling of angiogenesis activities of calycosin in zebrafish.Mol Biosyst. 2011 Nov;7(11):3112-21. doi: 10.1039/c1mb05206c. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Mol Biosyst. 2011. PMID: 21909574
-
Basal Flt1 tyrosine kinase activity is a positive regulator of endothelial survival and vascularization during zebrafish embryogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1850(2):373-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.10.023. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25450186
-
The Expanding Complexity of Estrogen Receptor Signaling in the Cardiovascular System.Circ Res. 2016 Mar 18;118(6):994-1007. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.305376. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 26838792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances of targeted therapy based on estrogen receptor signaling pathway in lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011 Sep;14(9):727-32. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.09.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21924040 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Perifosine as potential anti-cancer agent inhibits proliferation, migration, and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Sep;368(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0986-z. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 21769450
-
A critical courier role of volatile oils from Dalbergia odorifera for cardiac protection in vivo by QiShenYiQi.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 4;7(1):7353. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07659-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28779167 Free PMC article.
-
Astragali Radix Isoflavones Synergistically Alleviate Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Via Activating Estrogen Receptor-PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 22;12:533028. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.533028. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. Retraction in: Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 06;14:1252192. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1252192. PMID: 33692686 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Polysaccharides from astragali radix restore chemical-induced blood vessel loss in zebrafish.Vasc Cell. 2012 Feb 23;4(1):2. doi: 10.1186/2045-824X-4-2. Vasc Cell. 2012. PMID: 22357377 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo angiogenesis screening and mechanism of action of novel tanshinone derivatives produced by one-pot combinatorial modification of natural tanshinone mixture from Salvia miltiorrhiza.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e100416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100416. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24992590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franco CA, Liebner S, Gerhardt H. Vascular morphogenesis: a Wnt for every vessel? Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19:476–483. - PubMed
-
- Barkhem T, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA. Molecular mechanisms, physiological consequences and pharmacological implications of estrogen receptor action. Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2004;4:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Losordo DW, Isner JM. Estrogen and angiogenesis: A review. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Kim-Schulze S, McGowan KA, Hubchak SC, Cid MC, Martin MB, et al. Expression of an estrogen receptor by human coronary artery and umbilical vein endothelial cells. Circulation. 1996;94:1402–1407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

