The role of chemokines during viral infection of the CNS
- PMID: 20686655
- PMCID: PMC2912390
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000937
The role of chemokines during viral infection of the CNS
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
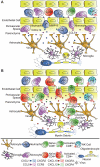
Figures
References
-
- Lane TE, Asensio VC, Yu N, Paoletti AD, Campbell IL, et al. Dynamic regulation of alpha- and beta-chemokine expression in the central nervous system during mouse hepatitis virus-induced demyelinating disease. J Immunol. 1998;160:970–978. - PubMed
-
- Christensen JE, Simonsen S, Fenger C, Sorensen MR, Moos T, et al. Fulminant lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-induced inflammation of the CNS involves a cytokine-chemokine-cytokine-chemokine cascade. J Immunol. 2009;182:1079–1087. - PubMed
-
- Aravalli RN, Hu S, Rowen TN, Palmquist JM, Lokensgard JR. Cutting edge: TLR2-mediated proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine production by microglial cells in response to herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 2005;175:4189–4193. - PubMed
-
- van Marle G, Henry S, Todoruk T, Sullivan A, Silva C, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein mediates neural cell death: a neurotoxic role for IP-10. Virology. 2004;329:302–318. - PubMed

