More than 1,001 problems with protein domain databases: transmembrane regions, signal peptides and the issue of sequence homology
- PMID: 20686689
- PMCID: PMC2912341
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000867
More than 1,001 problems with protein domain databases: transmembrane regions, signal peptides and the issue of sequence homology
Abstract
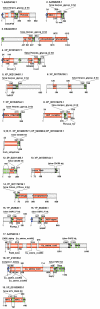
Large-scale genome sequencing gained general importance for life science because functional annotation of otherwise experimentally uncharacterized sequences is made possible by the theory of biomolecular sequence homology. Historically, the paradigm of similarity of protein sequences implying common structure, function and ancestry was generalized based on studies of globular domains. Having the same fold imposes strict conditions over the packing in the hydrophobic core requiring similarity of hydrophobic patterns. The implications of sequence similarity among non-globular protein segments have not been studied to the same extent; nevertheless, homology considerations are silently extended for them. This appears especially detrimental in the case of transmembrane helices (TMs) and signal peptides (SPs) where sequence similarity is necessarily a consequence of physical requirements rather than common ancestry. Thus, matching of SPs/TMs creates the illusion of matching hydrophobic cores. Therefore, inclusion of SPs/TMs into domain models can give rise to wrong annotations. More than 1001 domains among the 10,340 models of Pfam release 23 and 18 domains of SMART version 6 (out of 809) contain SP/TM regions. As expected, fragment-mode HMM searches generate promiscuous hits limited to solely the SP/TM part among clearly unrelated proteins. More worryingly, we show explicit examples that the scores of clearly false-positive hits, even in global-mode searches, can be elevated into the significance range just by matching the hydrophobic runs. In the PIR iProClass database v3.74 using conservative criteria, we find that at least between 2.1% and 13.6% of its annotated Pfam hits appear unjustified for a set of validated domain models. Thus, false-positive domain hits enforced by SP/TM regions can lead to dramatic annotation errors where the hit has nothing in common with the problematic domain model except the SP/TM region itself. We suggest a workflow of flagging problematic hits arising from SP/TM-containing models for critical reconsideration by annotation users.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
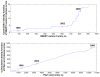
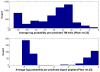
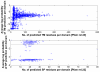
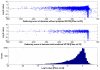
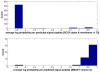
 is the database size,
is the database size,  and
and  are the extreme value distribution (EVD) parameters of the domain model. The bottom plot depicts the histogram of the 10340 domains in Pfam rel.23. The median of all log E-values that corresponded to the domain-specific GAs is found to be −1.16. This translates to an E-value of 0.07.
are the extreme value distribution (EVD) parameters of the domain model. The bottom plot depicts the histogram of the 10340 domains in Pfam rel.23. The median of all log E-values that corresponded to the domain-specific GAs is found to be −1.16. This translates to an E-value of 0.07.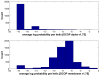
References
-
- Eisenhaber F. Prediction of Protein Function: Two Basic Concepts and One Practical Recipe. In: Eisenhaber F, editor. Discovering Biomolecular Mechanisms with Computational Biology. Georgetown and New York: Landes Biosciences and Springer; 2006. pp. 39–54.
-
- Sammut SJ, Finn RD, Bateman A. Pfam 10 years on: 10,000 families and still growing. Brief Bioinform. 2008;9:210–219. - PubMed
-
- Ivanov D, Schleiffer A, Eisenhaber F, Mechtler K, Haering CH, et al. Eco1 is a novel acetyltransferase that can acetylate proteins involved in cohesion. Curr Biol. 2002;12:323–328. - PubMed
-
- Bork P, Dandekar T, Diaz-Lazcoz Y, Eisenhaber F, Huynen M, et al. Predicting function: from genes to genomes and back. J Mol Biol. 1998;283:707–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

