Calpain 8/nCL-2 and calpain 9/nCL-4 constitute an active protease complex, G-calpain, involved in gastric mucosal defense
- PMID: 20686710
- PMCID: PMC2912385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001040
Calpain 8/nCL-2 and calpain 9/nCL-4 constitute an active protease complex, G-calpain, involved in gastric mucosal defense
Abstract
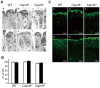
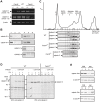
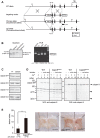
Calpains constitute a superfamily of Ca2+-dependent cysteine proteases, indispensable for various cellular processes. Among the 15 mammalian calpains, calpain 8/nCL-2 and calpain 9/nCL-4 are predominantly expressed in the gastrointestinal tract and are restricted to the gastric surface mucus (pit) cells in the stomach. Possible functions reported for calpain 8 are in vesicle trafficking between ER and Golgi, and calpain 9 are implicated in suppressing tumorigenesis. These highlight that calpains 8 and 9 are regulated differently from each other and from conventional calpains and, thus, have potentially important, specific functions in the gastrointestinal tract. However, there is no direct evidence implicating calpain 8 or 9 in human disease, and their properties and physiological functions are currently unknown. To address their physiological roles, we analyzed mice with mutations in the genes for these calpains, Capn8 and Capn9. Capn8(-/-) and Capn9(-/-) mice were fertile, and their gastric mucosae appeared normal. However, both mice were susceptible to gastric mucosal injury induced by ethanol administration. Moreover, the Capn8(-/-) stomach showed significant decreases in both calpains 9 and 8, and the same was true for Capn9(-/-). Consistent with this finding, in the wild-type stomach, calpains 8 and 9 formed a complex we termed "G-calpain," in which both were essential for activity. This is the first example of a "hybrid" calpain complex. To address the physiological relevance of the calpain 8 proteolytic activity, we generated calpain 8:C105S "knock-in" (Capn8(CS/CS)) mice, which expressed a proteolytically inactive, but structurally intact, calpain 8. Although, unlike the Capn8(-/-) stomach, that of the Capn8(CS/CS) mice expressed a stable and active calpain 9, the mice were susceptible to ethanol-induced gastric injury. These results provide the first evidence that both of the gastrointestinal-tract-specific calpains are essential for gastric mucosal defense, and they point to G-calpain as a potential target for gastropathies caused by external stresses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Gastrointestinal Calpain Complex, G-calpain, Is a Heterodimer of CAPN8 and CAPN9 Calpain Isoforms, Which Play Catalytic and Regulatory Roles, Respectively.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 30;291(53):27313-27322. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.763912. Epub 2016 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27881674 Free PMC article.
-
Both the conserved and the unique gene structure of stomach-specific calpains reveal processes of calpain gene evolution.J Mol Evol. 2001 Sep;53(3):191-203. doi: 10.1007/s002390010209. J Mol Evol. 2001. PMID: 11523006
-
[Physiological importance of calpains in gastric mucosal defense].Nihon Rinsho. 2011 Jun;69(6):1116-22. Nihon Rinsho. 2011. PMID: 21688638 Review. Japanese.
-
Stomach-specific calpain, nCL-2, localizes in mucus cells and proteolyzes the beta-subunit of coatomer complex, beta-COP.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 21;281(16):11214-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509244200. Epub 2006 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16476741
-
Regulation and physiological roles of the calpain system in muscular disorders.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Oct 1;96(1):11-22. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs157. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22542715 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calpain-mediated proteolysis as driver and modulator of polyglutamine toxicity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 19;15:1020104. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1020104. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36385755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro Model Systems for Studies Into Retinal Neuroprotection.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 7;16:938089. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.938089. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35873807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles and Particles Derived From Adipocytes: The Potential Role in Spreading MicroRNAs Associated With Cellular Senescence.Front Aging. 2022 Aug 9;3:867100. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.867100. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 36016863 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain 9 as a therapeutic target in TGFβ-induced mesenchymal transition and fibrosis.Sci Transl Med. 2019 Jul 17;11(501):eaau2814. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau2814. Sci Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31316008 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain-3-mediated regulation of the Na⁺-Ca²⁺ exchanger isoform 3.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Feb;468(2):243-55. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1747-8. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26503425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J. The calpain system. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:731–801. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Hata S, Kawabata Y, Sorimachi H. Structure, activation, and biology of calpain. Diabetes. 2004;53:S12–18. - PubMed
-
- Horikawa Y, Oda N, Cox NJ, Li X, Orho-Melander M, et al. Genetic variation in the gene encoding calpain-10 is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 2000;26:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Richard I, Broux O, Allamand V, Fougerousse F, Chiannilkulchai N, et al. Mutations in the proteolytic enzyme calpain 3 cause limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. Cell. 1995;81:27–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

