Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and nuclear imaging studies of 111In-labeled rGel/BLyS fusion toxin in SCID mice bearing B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 20686856
- PMCID: PMC6279425
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-010-0391-0
Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and nuclear imaging studies of 111In-labeled rGel/BLyS fusion toxin in SCID mice bearing B cell lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: We examined the biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of (111)In-labeled rGel/BLyS, a gelonin toxin (rGel)-B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) fusion protein.
Materials and methods: rGel/BLyS was labeled with In-111 through DTPA with a labeling efficiency >95%. Biodistribution/imaging studies were obtained in severe-combined immunodeficiency mice bearing diffuse large B cell lymphoma OCI-Ly10. Pharmacokinetic studies were performed in BALB/c mice.
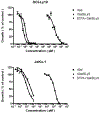
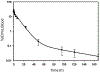
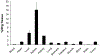
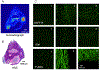
Results: In vitro, DTPA-conjugated rGel/BLyS displayed selective cytotoxicity against OCI-Ly10 cells and mantle cell lymphoma JeKo cells. In vivo, rGel/BLyS exhibited a tri-exponential disposition with a rapid initial mean distribution followed by an extensive mean distribution and a long terminal elimination phase. At 48 h after injection, uptake of the radiotracer in tumors was 1.25 %ID/g, with a tumor-to-blood ratio of 13. Tumors were clearly visualized at 24-72 h post-injection. Micro-SPECT-CT images and ex vivo analyses confirmed the accumulation of rGel/BLyS in OCI-Ly10 tumors.
Conclusions: (111)In-DTPA-rGel/BLyS are distributed to B cell tumors and induce apoptosis in tumors. Preclinical antitumor studies using rGel/BLyS should use a twice-per-week treatment schedule.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with an rGel/BLyS fusion toxin.Leukemia. 2012 Aug;26(8):1786-96. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.54. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Leukemia. 2012. PMID: 22373785 Free PMC article.
-
The rGel/BLyS fusion toxin inhibits diffuse large B-cell lymphoma growth in vitro and in vivo.Neoplasia. 2010 May;12(5):366-75. doi: 10.1593/neo.91960. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20454508 Free PMC article.
-
The rGel/BLyS fusion toxin specifically targets malignant B cells expressing the BLyS receptors BAFF-R, TACI, and BCMA.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Feb;6(2):460-70. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0254. Epub 2007 Jan 31. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17267661
-
111In-Labeled recombinant gelonin toxin-B lymphocyte stimulator protein fusion protein.2011 Feb 22 [updated 2011 Mar 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Feb 22 [updated 2011 Mar 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21473028 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
BLyS and B cell homeostasis.Semin Immunol. 2006 Oct;18(5):318-26. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Semin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16931037 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with an rGel/BLyS fusion toxin.Leukemia. 2012 Aug;26(8):1786-96. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.54. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Leukemia. 2012. PMID: 22373785 Free PMC article.
-
Split-design approach enhances the therapeutic efficacy of ligand-based CAR-T cells against multiple B-cell malignancies.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 11;15(1):9751. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54150-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39528513 Free PMC article.
-
A novel knowledge representation framework for the statistical validation of quantitative imaging biomarkers.J Digit Imaging. 2013 Aug;26(4):614-29. doi: 10.1007/s10278-013-9598-3. J Digit Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23546775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosome-inactivating proteins: from plant defense to tumor attack.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Nov;2(11):2699-737. doi: 10.3390/toxins2112699. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual functional BAFF receptor aptamers inhibit ligand-induced proliferation and deliver siRNAs to NHL cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(7):4266-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt125. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23470998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moore PA, Belvedere O, Orr A et al. (1999) BLyS: Member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science 285:260–263. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay A, Ni J, Zhai Y, Yu G-L, Aggarwal BB (1999) Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine, THANK, a TNF homologue that activates apoptosis, nuclear factor-kappaB, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem 274:15978–15981. - PubMed
-
- Shu HB, Hu WH, Johnson H (1999) TALL-1 is a novel member of the TNF family that is down-regulated by mitogens. J Leukoc Biol 65:680–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

