Antibiotic therapy for Shigella dysentery
- PMID: 20687081
- PMCID: PMC6532574
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006784.pub4
Antibiotic therapy for Shigella dysentery
Abstract
Background: Shigella dysentery is a relatively common illness and occasionally causes death, worldwide. Mild symptoms are self-limiting but in more severe cases, antibiotics are recommended for cure and preventing relapse. The antibiotics recommended are diverse, have regional differences in sensitivity, and have side effects.
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of antibiotics for treating Shigella dysentery.
Search strategy: In June 2009 we identified all relevant trials from the following databases: Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register; Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2008, issue 4), MEDLINE, EMBASE, LILACS and the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT). We also checked conference proceedings for relevant abstracts, and contacted researchers, organizations, and pharmaceutical companies.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials of antibiotics for Shigella dysentery.
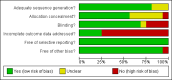
Data collection and analysis: Four authors, working in pairs, independently assessed trial eligibility, methodological quality, and extracted data. We calculated risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for dichotomous data, and used the random-effects model for significant heterogeneity. We explored possible sources of heterogeneity, when present, in subgroup analyses of participant age and percentage of participants with confirmed Shigella infection.
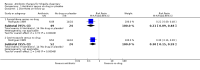
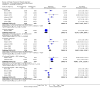
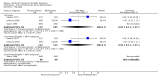
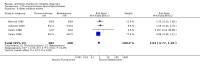
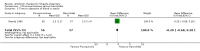
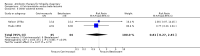
Main results: Sixteen trials (1748 participants), spanning four decades and with differing sensitivity to Shigella isolates, met the inclusion criteria. Seven were judged to be at risk of bias due to inadequate allocation concealment or blinding, and 12 due to incomplete reporting of outcome data. Limited data from one three-armed trial of people with moderately severe illness suggest that antibiotics reduce the episodes of diarrhoea at follow-up (furazolidone versus no drug RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.48, 73 participants; cotrimoxazole versus no drug RR 0.30, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.59, 76 participants).There was insufficient evidence to consider any class of antibiotic superior in efficacy in treating Shigella dysentery, but heterogeneity for some comparisons limits confidence in the results. All the antibiotics studied were safe. There was inadequate evidence regarding the role of antibiotics in preventing relapses.
Authors' conclusions: Antibiotics reduce the duration of Shigella dysentery.Regularly updated local or regional antibiotic sensitivity patterns to different species and strains of Shigella are required to guide empiric therapy. More trials adhering to standard guidelines are required to evaluate the role of antibiotics in the treatment of severe forms of Shigella dysentery and in groups who are at high risk of complications.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures



























Update of
-
Antibiotic therapy for Shigella dysentery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD006784. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006784.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Aug 04;(8):CD006784. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006784.pub4. PMID: 20091606 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Alam 1994 {published data only}
-
- Alam AN, Islam MR, Hossain MS, Mahalanabis D, Hye HKMA. Comparison of pivmecillinam and nalidixic acid in the treatment of acute shigellosis in children. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1994;29(4):313‐7. - PubMed
Bennish 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bennish ML, Salam MA, Haider R, Barza M. Therapy for shigellosis. II. Randomized, double‐blind comparison of ciprofloxacin and ampicillin. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1990;162(3):711‐6. - PubMed
Bibile 1961 {published data only}
-
- Bibile SW, Cooray MPM, Balasubramaniam K, Gulasekaram J. Comparative trial of drugs in bacillary dysentery. Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygeine 1961;64:300‐2. - PubMed
Dutta 1995 {published data only}
-
- Dutta P, Sett A, Sarkar A, Mitra U, Saha D, Manna B, et al. Comparative efficacy of furazolidone and nalidixic acid in the empirical treatment of acute invasive diarrhoea: randomised clinical trial. Indian Pediatrics 1995;32(1):13‐9. - PubMed
Gotuzzo 1989 {published data only}
Haltalin 1973 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Islam 1994 {published data only}
-
- Islam MR, Alam AN, Hossain, MS, Mahalanabis D, Hye HK. Double‐blind comparison of oral gentamicin and nalidixic acid in the treatment of acute shigellosis in children. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1994;40(6):320‐5. - PubMed
Kabir 1986 {published data only}
Khan 1997a {published data only}
-
- Khan WA, Seas C, Dhar U, Salam MA, Bennish ML. Treatment of shigellosis: V. Comparison of Azithromycin and Ciprofloxacin: A Double‐Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997;126(9):697‐703. - PubMed
Leibovitz 2000 {published data only}
-
- Leibovitz E, Janco J, Piglansky L, Press J, Yagupsky P, Reinhart H, et al. Oral ciprofloxacin vs. intramuscular ceftriaxone as empiric treatment of acute invasive diarrhoea in children. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2000;19(11):1060‐7. - PubMed
Nelson 1976a {published data only}
-
- Nelson JD, Kusmiesz H, Jackson LH, Woodman E. Trimethoprim‐sulfamethoxazole therapy for shigellosis. JAMA 1976;235(12):1239‐43. - PubMed
Prado 1993 {published data only}
-
- Prado D, Liu H, Velasquez T, Cleary TG. Comparative efficacy of pivmecillinam and cotrimoxazole in acute shigellosis in children. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1993;25(6):713‐9. - PubMed
Rodriguez 1989 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Rodriguez RS, Chavez AZ, Galindo E. A randomised, controlled, single‐blind study comparing furazolidone with trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole in the empirical treatment of acute invasive diarrhoea. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. Supplement 1989;169:47‐53. - PubMed
Salam 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Salam MA, Bennish ML. Therapy for shigellosis. I. Randomised, double‐blind trial of nalidixic acid in childhood shigellosis. Journal of Pediatrics 1988;113(5):901‐7. - PubMed
Salam 1998 {published data only}
-
- Salam MA, Dhar U, Khan WA, Bennish ML. Randomised comparison of ciprofloxacin suspension and pivmecillinam for childhood shigellosis. Lancet 1998;352:522‐7. - PubMed
Shanks 1999 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Shanks GD, Smoak BL, Aleman GM, Oundo J, Waiyaki PG, Dunne MW, et al. Single dose of azithromycin or three‐day course of ciprofloxacin as therapy for epidemic dysentery in Kenya. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1999;29(4):942‐3. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aoki 1987 {published data only}
-
- Aoki T, Shimizu N, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Matsubara Y, Seo T, et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy of norfloxacin (NFLX) and pipemidic acid (PPA) in the treatment of infectious enteritis by a double‐blind method. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1987;61(7):830‐48. - PubMed
Aoki 1989 {published data only}
-
- Aoki T, Shimizu N, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Matsubara Y, Nitta Y, et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy of lomefloxacin (LFLX, NY‐198) and pipemidic acid (PPA) in the treatment of infectious enteritis by a double‐blind method. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1989;63(6):606‐22. - PubMed
Ashkenazi 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ashkenazi S, Amir J, Waisman Y, Rachmel A, Garty BZ, Samra Z, et al. A randomised, double‐blind study comparing cefixime and trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole in the treatment of childhood shigellosis. The Journal of Pediatrics 1993;123(5):817‐21. [ISSN: CN‐00096970] - PubMed
Barada 1980 {published data only}
Bassily 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bassily S, Hyams K C, Masry NA, Farid Z, Cross E, Bourgeois AL, Ayad E, Hibbs RG. Short‐course norfloxacin and trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole treatment of shigellosis and salmonellosis in Egypt. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1994;51(2):219‐23. - PubMed
Basualdo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Basualdo W, Arbo A. Randomized comparison of azithromycin versus cefixime for treatment of shigellosis in children. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2003;22(4):374‐7. - PubMed
Bennish 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bennish ML, Salam MA, Khan WA, Khan AM. Treatment of shigellosis: III. Comparison of one‐ or two‐dose ciprofloxacin with standard 5‐day therapy. A randomised, blinded trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1992;117(9):727‐34. - PubMed
Bezjak 1966 {published data only}
-
- Bezjak B, Breitenfeld V. Therapy of shigellosis and chronic intestinal amoebiasis with enterosediv [Die Therapie der Shigellose und der chronischen Intestinal amoebiasis mit Enterosediv]. Therapie Der Gegenwart 1966;103(9):1129‐36. - PubMed
Bhattacharya 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bhattacharya SK, Bhattacharya MK, Dutta P, Sen D, Rasaily R, Moitra A, et al. Randomized clinical trial of norfloxacin for shigellosis. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1991;45(6):683‐7. - PubMed
Bhattacharya 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bhattacharya MK, Nair GB, Sen D, Paul M, Debnath A, Nag A, et al. Efficacy of norfloxacin for shigellosis: a double‐blind randomised clinical trial. Journal of Diarrhoeal Diseases Research 1992;10(3):146‐50. - PubMed
Bhattacharya 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bhattacharya K, Bhattacharya MK, Dutta D, Dutta S, Deb M, Deb A, et al. Double‐blind, randomised clinical trial for safety and efficacy of norfloxacin for shigellosis in children. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86(3):319‐20. - PubMed
Bogaerts 1985 {published data only}
-
- Bogaerts J, Habyalimana JB, Chevolet T, Vandepitte J. Treatment of severe bacillary dysentery with trimethoprim alone. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1985;79(2):203‐5. - PubMed
Browne 1983 {published data only}
-
- Robins‐Browne RM, Coovadia HM, Bodasing MN, Mackenjee MKR. Treatment of acute nonspecific gastroenteritis of infants and young children with erythromycin. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1983;32(4):886‐90. - PubMed
Brugel 1950 {published data only}
-
- Brügel H. On the treatment of bacillary dysentery with phages specific for the endemic infection [Über die Behandlung der Bazillen‐Ruhr mit epidemiespezifischen Ruhrphagen]. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 1950;75(51):1751‐2. - PubMed
Butler 1993 {published data only}
-
- Butler T, Lolekha S, Rasidi C, Kadio A, Rosal PL, Iskandar H, et al. Treatment of acute bacterial diarrhoea: a multicenter international trial comparing placebo with fleroxacin given as a single dose or once daily for 3 days. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(3A):187S‐194S. - PubMed
Cabada 1992 {published data only}
-
- Cabada FJ, DuPont HL, Gyr K, Mathewson JJ. Antimicrobial therapy of bacterial diarrhoea in adult residents of Mexico ‐ lack of an effect. Digestion 1992;53(3‐4):134‐41. - PubMed
Camacho 1989 {published data only}
-
- Camacho JLP. A comparison of furazolidone and ampicillin in the treatment of invasive diarrhoea. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 1989;16(Suppl):954‐9. - PubMed
CDC 2006 {published data only}
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update on emerging infections: news from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2006;47(1):106‐9. - PubMed
Chang 1977 {published data only}
-
- Chang MJ, Dunkle LM, Reken D, Anderson D, Wong ML, Feigin RD. Trimethoprim‐sulfamethoxazole compared to ampicillin in the treatment of shigellosis. Pediatrics 1977;59(5):726‐9. - PubMed
de Olarte 1974 {published data only}
-
- Garcia de Olarte D, Trujillo H, Agudelo N, Nelson JD, Haltalin KC. Treatment of diarrhoea in malnourished infants and children. A double‐blind study comparing ampicillin and placebo. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1974;127(3):379‐88. - PubMed
Dryden 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dryden MS, Gabb RJ, Wright SK. Empirical treatment of severe acute community‐acquired gastroenteritis with ciprofloxacin. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1996;22(6):1019‐25. - PubMed
Dumitriu 1992 {published data only}
-
- Dumitriu S, Dumitriu M, Dimitriu SM, Turcu T, Grigore L, Dumitriu D, et al. Bioactive polymers: in vitro and in vivo study of controlled release neomycin. Journal of Biomaterials Applications 1992;6(3):251‐60. - PubMed
DuPont 1973 {published data only}
-
- DuPont HL, Hornick RB. Adverse effect of lomotil therapy in shigellosis. JAMA 1973;226(13):1525‐8. - PubMed
DuPont 1982 {published data only}
-
- DuPont HL, Reves RR, Galindo E, Sullivan PS, Wood LV, Mendiola JG. Treatment of travellers' diarrhoea with trimethoprim/sulphamethoxazole and with trimethoprim alone. New England Journal of Medicine 1982;307(14):841‐4. - PubMed
DuPont 1983 {published data only}
-
- Dupont HL, Ericsson CD, Galindo E, Dupont MW, Mendiola Gomez J. Antimicrobial therapy of travellers' diarrhoea. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;84(Suppl):99‐105. - PubMed
DuPont 1984 {published data only}
DuPont 1986 {published data only}
-
- DuPont HL, Ericsson CD, Reves RR, Galindo E. Antimicrobial therapy for travellers' diarrhoea. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1986;8(Suppl 2):S217‐22. - PubMed
DuPont 1992 {published data only}
DuPont 1992a {published data only}
-
- DuPont HL, Ericsson CD, Mathewson JJ, Cabada FJ, Conrad DA. Oral aztreonam, a poorly absorbed yet effective therapy for bacterial diarrhoea in US travellers to Mexico. JAMA 1992;267(14):1932‐5. - PubMed
Ekwall 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ekwall E, Jonsson M. A comparison of the combination pivmecillinam/pivampicillin and co‐trimoxazole in the treatment of convalescent carriers of Salmonella and Shigella. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1984;16(1):99‐102. - PubMed
Ericsson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Ericsson CD, DuPont HL, Sullivan P, Galindo E, Evans DG, Evans DJJr. Bicozamycin, a poorly absorbable antibiotic, effectively treats travellers' diarrhoea. Annals of Internal Medicine 1983;98(1):20‐5. - PubMed
Ericsson 1992 {published data only}
Fakouhi 1971 {published data only}
-
- Fakouhi T, Post C, Dutz W. Clinical trial with sulphamethoxazole‐trimethoprim in infantile gastroenteritis. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1971;13(1):13‐7. - PubMed
Gendrel 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gendrel D, Moreno JL, Nduwimana M, Baribwira C, Raymond J. One‐dose treatment with pefloxacin for infection due to multidrug‐resistant Shigella dysenteriae type I in Burundi. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1997;24(1):83. - PubMed
Gilman 1980 {published data only}
Gilman 1981 {published data only}
-
- Gilman RH, Spira W, Rabbani H, Ahmed W, Islam A, Rahaman MM. Single‐dose ampicillin therapy for severe shigellosis in Bangladesh. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1981;143(2):164‐9. - PubMed
Goodman 1990 {published data only}
-
- Goodman LJ, Trenholme GM, Kaplan RL, Segreti J, Hines D, Petrak R, et al. Empiric antimicrobial therapy of domestically acquired acute diarrhoea in urban adults. Archives of Internal Medicine 1990;150(3):541‐6. - PubMed
Ha 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ha V. A randomised controlled trial of gatifloxacin versus ciprofloxacin for the treatment of bacillary dysentery in children. http://isrctn.org/ISRCTN55945881 (accessed 14 October 2008). [ISRCTN55945881; Wellcome Trust reference: 061330]
Haltalin 1967 {published data only}
-
- Haltalin KC, Nelson JD, Ring R, Sladoje M, Hinton LV. Double‐blind treatment study of shigellosis comparing ampicillin, sulphadiazine, and placebo. Journal of Pediatrics 1967;70(6):970‐81. - PubMed
Haltalin 1968 {published data only}
-
- Haltalin KC, Nelson JD, Hinton LV, Kusmiesz HT, Sladoje M. Comparison of orally absorbable and non‐absorbable antibiotics in shigellosis. A double‐blind study with ampicillin and neomycin. The Journal of Pediatrics 1968;72(5):708‐20. - PubMed
Haltalin 1968a {published data only}
-
- Haltalin KC, Nelson JD, Kusmiesz HT, Hinton LV. Comparison of intramuscular and oral ampicillin therapy for shigellosis. Journal of Pediatrics 1968;73(4):617‐22. - PubMed
Haltalin 1969 {published data only}
-
- Haltalin KC, Nelson JD, Kusmies, HT, Hinton LV. Optimal dosage of ampicillin for shigellosis. The Journal of Pediatrics 1969;74(4):626‐31. - PubMed
Haltalin 1972 {published data only}
-
- Haltalin KC, Nelson JD. Failure of furazolidone therapy in shigellosis. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1972;123(1):40‐4. - PubMed
Haltalin 1972a {published data only}
-
- Haltalin KC, Kusmiesz HT, Hinton LV, Nelson JD. Treatment of acute diarrhoea in outpatients. Double‐blind study comparing ampicillin and placebo. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1972;124(4):554‐61. - PubMed
Han 1998 {published data only}
-
- Han CR, Li SL, Luo DD. Comparation of rufloxacin with homefloxacin in 30 cases of bacillary dysentery. Journal of Clinical Internal Medicine 1998;15(2):88.
Hansson 1981 {published data only}
-
- Hansson HB, Barkenius G, Cronberg S, Juhlin I. Controlled comparison of nalidixic acid or lactulose with placebo in shigellosis. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1981;13(3):191‐3. - PubMed
Helvaci 1998 {published data only}
-
- Helvaci M, Bektaslar D, Ozkaya B, Yaprak I, Umurtak B, Ertugrul A. Comparative efficacy of cefixime and ampicillin‐sulbactam in shigellosis in children. Acta Paediatrrica Japonica 1998;40:131‐4. - PubMed
Hiraishi 1980 {published data only}
-
- Hiraishi K, Matsubara Y. Comparison of clinical efficacy of fosfomycin (FOM) and kanamycin (KM) in bacillary dysentery by double blind method. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1980;54(7):343‐52. - PubMed
Imagawa 1988 {published data only}
-
- Imagawa Y, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Ito K, Matsubara Y, Seo T, et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy of ciprofloxacin (CPFX, BAY o 9867) and pipemidic acid (PPA) in the treatment of infectious enteritis by a double‐blind method. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1988;62(4):322‐39. - PubMed
Iushchuk 2007 {published data only}
-
- Iushchuk ND, Maev IV, Mar'ianovskaia TV, Gagarina IV. Using neosmectin in the complex therapy of patients with acute intestinal infections. Experimental & Clinical Gastroenterology 2007;2:126‐30. - PubMed
Jiang 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jiang SC, Wang XF, Miao JZ. Clinical efficacy of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin. Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine 1994;33(7):444‐8. - PubMed
Jiang 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jiang XP, Ye Y. Therapeutic effect of phosphonomycin combined with another antibiotic on shigellosis. Journal of Clinical Internal Medicine 2000;17(1):48.
Jinhua 1992 {published data only}
-
- Jinhua L, Ziaofeng W, Suchum J. Effect observation of pefloxacin in treatment of 64 patients with acute bacillary dysentery. Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases 1992;10(Suppl 2):116‐8.
Kabir 1984 {published data only}
Legros 2004 {published data only}
-
- Legros D, Fontaine O. Shigellosis: report of a workshop, held at ICDDR,B: Centre for Health and Population Research, Dhaka, Bangladesh, on 16‐18 February 2004. Journal of Health, Population & Nutrition 2004;22(4):445‐9. - PubMed
Lexomboon 1972 {published data only}
Lionel 1969 {published data only}
-
- Lionel ND, Abeyasekera FJ, Samarasinghe HG, Goonewardena CV, Tawil GS. A comparison of a single dose and a five day course of tetracycline therapy in bacillary dysentery. Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1969;72(7):170‐2. - PubMed
Lolekha 1988 {published data only}
-
- Lolekha S, Patanachareon S, Thanangkul B, Vibulbandhitkit S. Norfloxacin versus co‐trimoxazole in the treatment of acute bacterial diarrhoea: a placebo controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases. Supplementum 1988;56:35‐45. - PubMed
Lolekha 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lolekha S, Vibulbandhitkit S, Poonyarit P. Response to antimicrobial therapy for shigellosis in Thailand. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1991;13(Suppl 4):S342‐6. - PubMed
Mabadeje 1974 {published data only}
-
- Mabadeje AF. A controlled clinical trial of trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole in shigella dysentery. Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1974;77(3):50‐4. - PubMed
Mahllooji 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mahllooji KH. A comparative study of cefixime and nalidixic acid, against Shigella in Children Hospital Medical Center of Ali Asghar in Tehran‐Iran during 1999. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2004;8(Suppl 1):S17.
Martin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Martin JM, Pitetti R, Maffei R, Tritt J, Smail K, Wald ER. Treatment of shigellosis with cefixime: two days vs. five days. Pediatric Infectious Diseases Journal 2000;19:522‐6. - PubMed
Matsuoka 1995 {published data only}
-
- Matsuoka Y, Irimajiri S, Obana M, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Nitta Y, et al. Clinical study on the effects of grepafloxacin on infectious enteritis assessment of the fecal drug level and intestinal bacterial flora in a patient with infectious enteritis. Japanese Journal of Chemotherapy 1995;43(Suppl 1):319‐32.
Miles 1977 {published data only}
-
- Miles RN. Bacillary dysentery in Cyprus. Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps 1977;12:342‐4.
Mol 1987 {published data only}
-
- Mol P, Mets T, Lagasse R, Vandepitte J, Mutwewingabo A, Butzler JP. Treatment of bacillary dysentery: a comparison between enoxacin and nalidixic acid. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987;19(5):695‐8. - PubMed
Moolasart 1999 {published data only}
-
- Moolasart P, Eampokalap B, Ratanasrithong M. Comparison of the efficacy of ceftibuten and norfloxacin in the treatment of acute gastrointestinal infection in children. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1999;30(4):764‐9. - PubMed
Morisawa 1970 {published data only}
-
- Morisawa T. Clinical effects of Diromo on intestinal diseases (studies by double blind test). Japanese Archives of Internal Medicine 1970;17(4):99‐102. - PubMed
Motohiro 1982 {published data only}
-
- Motohiro T, Sakata Y, Fujimoto T. Evaluation of the effect of pipemidic acid on enteritis. A double blind controlled study compared with piromidic acid. Chemotherapy 1982;30(2):125‐48.
Nelson 1975 {published data only}
Nelson 1976 {published data only}
-
- Nelson JD, Kusmiesz H, Jackson LH. Comparison of trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole and ampicillin therapy for shigellosis in ambulatory patients. Journal of Pediatrics 1976;89(3):491‐3. - PubMed
Nikorowitsch 1978 {published data only}
-
- Nikorowitsch E. Length of stay in the hospital in shigella and salmonella infections treated with furazolidone and without any antimicrobial chemotherapy [Krankenhausverweildauer von Shigellosen und Salmonellosen bei Behandlung mit Furazolidon und ohne antimikrobielle Chemotherapie]. Zeitschrift Für Die Gesamte Innere Medizin Und Ihre Grenzgebiete 1978;33(2):51‐4. - PubMed
Oldfield 1987 {published data only}
-
- Oldfield EC, Bourgeois AL, Omar AK, Pazzaglia GL. Empirical treatment of Shigella dysentery with trimethoprim: five day course vs. single dose. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1987;37(3):616‐23. - PubMed
Orenstein 1981 {published data only}
-
- Orenstein WA, Ross L, Overturf GD, Wilkins J, Redfield DR, Underman A. Antibiotic treatment of acute shigellosis: failure of cefamandole compared with trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole and ampicillin. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1981;282(1):27‐33. - PubMed
Ostrower 1979 {published data only}
-
- Ostrower VG. Comparison of cefaclor and ampicillin in the treatment of shigellosis. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1979;55(Suppl):482‐4. - PubMed
Petruccelli 1992 {published data only}
-
- Petruccelli BP, Murphy GS, Sanchez JL, Walz S, DeFraites R, Gelnett J, et al. Treatment of traveller's diarrhoea with ciprofloxacin and loperamide. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1992;165(3):557‐60. - PubMed
Pichler 1986 {published data only}
-
- Pichler H, Diridl G, Wolf D. Ciprofloxacin in the treatment of acute bacterial diarrhoea: a double blind study. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986;5(2):241‐3. - PubMed
Pichler 1987 {published data only}
-
- Pichler HE, Diridl G, Stickler K, Wolf D. Clinical efficacy of ciprofloxacin compared with placebo in bacterial diarrhoea. American Journal of Medicine 1987;82(4A):329‐32. - PubMed
Prado 1981 {published data only}
-
- Prado V, Cohen J, Harun A, Aguirre X, Diaz C. Comparative randomised study on the clinico‐bacteriological effectiveness of mecillinam versus cotrimoxazole in shigellosis. Revista Chilena de Pediatría 1981;52(2):118‐24. - PubMed
Prado 1992 {published data only}
-
- Prado D, Lopez E, Liu H, Devoto S, Woloj M, Contrini M, et al. Ceftibuten and trimethoprim‐sulphamethoxazole for treatment of Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli disease. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1992;11(8):644‐7. - PubMed
Rabbani 1982 {published data only}
-
- Rabbani GH, Gilman RH, Spira WM. Single dose ampicillin therapy for the treatment of Shigellosis in Bangladesh. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1982;13(3):505‐6.
Rakhmanova 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rakhmanova AG, Kulikov VP. Treatment of Flexner's dysentery with ofloxacin [Lechenie dizenterii Fleksnera ofloksatsinom]. Antibiotiki i Khimioterapii 1996;41(9):95. - PubMed
Raqib 2008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Raqib R. Therapeutic induction of endogenous antibiotics for improved recovery in shigellosis. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00800930 (accessed 9 December 2008).
Rogerie 1986 {published data only}
Sagara 1993 {published data only}
-
- Sagara H, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Yamaguchi T, Masuda G, Negishi I, et al. Clinical study of temafloxacin on infectious enteritis. Chemotherapy 1993;41(Suppl. 5):464‐78.
Sagara 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sagara H, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Nitta Y, Tsunoda T, Yamaguchi T, et al. Basic and clinical studies of fleroxacin on infectious enteritis. Research Group of AM‐833 on infectious enteritis. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1994;68(11):1390‐408. - PubMed
Saito 1983 {published data only}
-
- Saito M, Tomizawa I, Konishi K, Takizawa Y, Matsubara Y, Seo T, et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy of pipemidic acid (PPA) and kanamycin (KM) in bacillary dysentery by double blind method. Kansenshogaku Zasshi 1983;57(4):303‐17. - PubMed
Saito 1984 {published data only}
-
- Saito M, Seo T, Matsubara Y, Tomizawa I, Takizawa Y, Ito K, et al. Comparison of clinical efficacy of ofloxacin COFLX: DL‐8280) and pipemidic acid (PPA) in acute infectious diarrhoea by a double‐blind method. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1984;58(10):965‐81. - PubMed
Salam 1995 {published data only}
-
- Salam MA, Seas C, Khan WA, Bennish ML. Treatment of shigellosis: IV. Cefixime is ineffective in shigellosis in adults. Annals of Internal Medicine 1995;123(7):505‐8. - PubMed
Salam 1999 {published data only}
Sepp 1995 {published data only}
-
- Sepp E, Tamm E, Torm S, Lutsar I, Mikelsaar M, Salminen S. Impact of a Lactobacillus probiotic on the faecal microflora in children with Shigellosis. Microecology and Therapy 1995;23:74‐80.
Seto 1992 {published data only}
-
- Seto WH, Lau FL, Gotuzzo EH, Carillo C. Lomefloxacin versus trimethoprim/sulphamethoxazole in the treatment of adults with acute bacterial diarrhoea. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 1992;2(1):61‐6. - PubMed
Soares 1994 {published data only}
-
- Soares JL, Arendt V, Coue JC, Milleliri JM, Philips B, Regis R, et al. Short‐term ciprofloxacin treatment of bacillary dysentery due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1 in Rwandan refugees [Traitement court par la ciprofloxacine de la dysenterie bacillaire à Shigella dysenteriae type 1 chez des réfugiés Ruandais]. Médecine Tropicale: Revue Du Corps De Santé Colonial 1994;54(4):319‐23. - PubMed
Soares 1996 {published data only}
-
- Soares JL, Milleliri JM, Pigny N, Dupoux J, Coue JC. Efficacy of bacillare dysentery's treatment by lomefloxacine amongst Rwandese refugees in North Zaire [Efficacité du traitement de la dysenterie bacillaire par lomefloxacine chez des refugies au Nord‐Zaire]. Medecine et Maladies Infectieuses 1996;26(2):141‐4.
Study Group 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zimbabwe, Bangladesh, South Africa (Zimbasa) Dysentery Study Group. Multicenter, randomised, double blind clinical trial of short course versus standard course oral ciprofloxacin for Shigella dysenteriae type 1 dysentery in children. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2002;21(12):1136‐41. - PubMed
Tian 1986 {published data only}
-
- Tian HY, Zhang XM, Zhou JQ. Effectiveness of swertia davidi and TMP in treating 75 cases of acute bacillary dysentery. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 1986;6(1):34‐5. - PubMed
Tong 1970 {published data only}
-
- Tong MJ, Martin DG, Cunningham JJ, Gunning JJ. Clinical and bacteriological evaluation of antibiotic treatment in shigellosis. JAMA 1970;214(10):1841‐4. - PubMed
Varsano 1991 {published data only}
-
- Varsano I, Eidlitz‐Marcus T, Nussinovitch M, Elian I. Comparative efficacy of ceftriaxone and ampicillin for treatment of severe shigellosis in children. Journal of Pediatrics 1991;118(4 (Pt 1)):627‐32. - PubMed
Vinh 2000 {published data only}
-
- Vinh H, Wain J, Chinh MT, Tam CT, Trang PT, Nga D, et al. Treatment of bacillary dysentery in Vietnamese children: two doses of ofloxacin versus 5‐days nalidixic acid. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2000;94(3):323‐6. - PubMed
Wistrom 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wistrom J, Jertborn M, Ekwall E, Norlin K, Soderquist B, Stromberg A, et al. Swedish study Group. Empiric treatment of acute diarrhoeal disease with norfloxacin. A randomised, placebo‐controlled study.. Annals of Internal Medicine 1992;117(3):202‐8. - PubMed
Xiouying 1986 {published data only}
-
- Xiouying WU, Juanfeng LU, Ruiyun YE. Therapeutic effect of pipemidic acid in the treatment of bacillary dysentery in children. Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases 1986;4(Suppl 4):736‐7.
Yamamoto 1973 {published data only}
-
- Yamamoto T, Tsunoda O, Sugiyama S, Nakajima K, Akao M. Effects of lividomycin on bacillary dysentery and related disorders. Comparison with the effects of kanamycin by a double blind method. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. Journal of the Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases 1973;47(2):35‐43. - PubMed
Ye 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ye XL, Cao YX, Xu JS, Wu KY, Shi XY. Multi‐drug‐resistant Shigella infections in Fujian Province, China. Journal of Diarrhoeal Diseases Research 1990;8(3):99. - PubMed
Yin 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lu Y, Cheng GX. A clinical investigation of treatment of acute bacillary dysentery with ceftriaxone in 84 children. New Chinese Medicine 1998;29(3):130‐1.
Yunus 1982 {published data only}
-
- Yunus M, Rahman ASMM, Farooque AS, Glass RI. Clinical trial of ampicillin v. trimethoprim sulphamethoxazole in the treatment of Shigella dysentery. Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1982;85(5):195‐9. - PubMed
Yuying 1995 {published data only}
-
- Yuying M, Guirong L, Guiqing D, Shuying Y. Clinical efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of 29 cases acute bacterial dysentery. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics 1995;20(2):110‐1.
Zhang 1991 {published data only}
-
- Zhang YY, Zhun BY, Jiang SC. Clinical evaluation of enoxacin. Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine 1991;30(8):480‐3, 521. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Carbo 1981 {published data only}
-
- Carbo L. Report of a clinical study of the therapeutic agent Ro/12/2510 vs. ampicillin in acute bacillary dysentery by Shigella [Reporte del estudio clinico del agente terapeutico Ro‐12‐2510 vs. ampicilina en cuadros de disenteria bacilar aguda por Shigella]. Investigación Médica Internacional 1981;8(2):191‐3.
Additional references
Baer 1999
BNF 2007
-
- British National Formulary (BNF 53). www.bnf.org/bnf March 2007 (accessed 13 June 2007).
Bogaerts 1983
-
- Bogaerts J, Verhaegen J, Munyabikali JP, Mukantabana B, Lemmens P, Vandeven J, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and serotypes of Shigella isolates in Kigali, Rwanda (1983 to 1993): increasing frequency of multiple resistance. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 1997;28(4):165‐71. - PubMed
CDC 2005
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases. Shigellosis. www.cdc.gov/node.do/id/0900f3ec8000755c 13 October 2005 (accessed 13 June 2007).
CONSORT 2008
-
- The CONSORT Statement. Available at http://www.consort‐statement.org (accessed 15 November 2008).
Datta 2003
-
- Datta D, Bhattacharya MK, Dutta S, Daatta A, Sarkar D, Bhandra B. Emergence of multidrug resistant Shigella dysenteriae type 1 causing sporadic outbreak in and around Kolkata, India. Journal of Health, Population, and Nutrition 2003;21(1):79‐80. - PubMed
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins, JPT, Altman DG, editors. Analysing and presenting results. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]; Section 8. www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm (accessed 31 May 2005).
Dutta 2002
GRADE 2004 [Computer program]
-
- Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. GRADE Working Group, 2004.
Gupta 2004
-
- Gupta A, Polyak CS, Bishop RD, Sobel J, Mintz ED. Laboratory‐confirmed shigellosis in the United States, 1989‐2002: epidemiologic trends and patterns. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2004;38(10):1372‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 (updated September 2008). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Huebner 1993
-
- Huebner J, Czerwenka W, Gruner E, Graevenitz A. Shigellemia in AIDS patients: case report and review of the literature. Infection 1993;21(2):122‐4. - PubMed
Juni 2001
Kosek 2008
Kotloff 1999
Kuo 2008
-
- Kuo CY, Su LH, Perera J, Carlos C, Tan BH, Kumarasinghe G, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Shigella isolates in eight Asian countries, 2001‐2004. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection 2008;41:107‐11. - PubMed
Mates 2000
-
- Mates A, Eyny D, Philo S. Antimicrobial resistance trends in Shigella serogroups isolated in Israel, 1990 ‐ 1995. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2000;19(2):108‐11. - PubMed
Niyogi 2005
-
- Niyogi SK. Shigellosis. Journal of Microbiology 2005;43(2):133‐43. - PubMed
Park 2005
-
- Park K. Park's textbook of preventive and social medicine. 18th Edition. Jabalpur: M/S Banarsidas Bhanot Publishers, 2005.
Pazhani 2004
Pazhani 2008
-
- Pazhani GP, Niyogi SK, Singh AK, Sen B, Taneja N, Kundu M, et al. Molecular characterization of multidrug‐resistant Shigella species isolated from epidemic and endemic cases of shigellosis in India. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2008;57:856‐63. - PubMed
Review Manager 2008 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.0. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Sarkar 2003
-
- Sarkar K, Ghosh S, Nujogi SK, Bhattacharya SK. Shigella dysenteriae type 1 with reduced susceptibility to flouroquinolones. Lancet 2003;361(9359):785. - PubMed
Shane 2003
-
- Shane AL, Tucker NA, Crump JA, Mintz ED, Painter JA. Sharing Shigella: risk factors and costs of a multi‐community outbreak of shigellosis. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(6):601‐3. - PubMed
Shiferaw 2004
-
- Shiferaw B, Shallow S, Marcus R, Segler S, Soderlund D, Hardnett FP, et al. Emerging Infections Program FoodNet Working Group. Trends in population‐based active surveillance for shigellosis and demographic variability in FoodNet sites, 1996‐1999. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2004;38 Suppl 3:175‐80. - PubMed
Sinha 1987
-
- Sinha AK, Bhattacharya SK, Sen D, Sengupta PG, Pal SC. Leukemoid reaction in Shigella dysenteriae type 1 infections. Indian Journal of Medical Research 1987;85:500‐2. - PubMed
Sire 2008
-
- Sire JM, Macondo EA, Clude JDPG, Siby T, Bahsoun I, Seck A, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in Shigella species isolated in Dakar, Senegal (2004‐2006). Japanese Journal of Infectious Disease 2008;61:307‐9. - PubMed
StatCalc 2006 [Computer program]
-
- Krishnamurthy K. StatCalc 2.0. University of Louisiana at Lafayette, 2006.
Sur 2003
Sur 2004
-
- Sur D, Ramamurthy T, Deen J, Bhattacharya SK. Shigellosis: challenges and management issues. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2004;120(5):454‐62. - PubMed
Talukder 2004
-
- Talukder KA, Khajanchi BK, Islam MA, Dutta DK, Islam Z, et al. Genetic relatedness of ciprofloxacin‐resistant Shigella dysenteriae type 1 strains isolated in south Asia. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2004;54(4):730‐4. - PubMed
Thorpe 2001
von Seidlein 2006
WHO 2005a
-
- World Health Organization. Dept. of Child and Adolescent Health and Development. Guidelines for the control of Shigellosis, including epidemics due to Shigella dysenteriae type 1. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2005.
WHO 2005b
-
- World Health Organization. Shigellosis: disease burden, epidemiology and case management. Weekly Epidemiological Record 2005;80(11):94‐9. - PubMed
WHO 2006
-
- World Health Organization. Shigella: Disease burden. www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/shigella/en (accessed 15 September 2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

