Genetic and pharmacological evidence for schizophrenia-related Disc1 interaction with GSK-3
- PMID: 20687111
- PMCID: PMC4485461
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20839
Genetic and pharmacological evidence for schizophrenia-related Disc1 interaction with GSK-3
Abstract
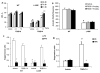
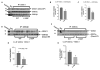
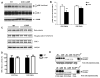
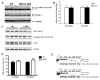
Recent studies have identified disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 (DISC1) as a strong genetic risk factor associated with schizophrenia. Previously, we have reported that a mutation in the second exon of the DISC1 gene [leucine to proline at amino acid position 100, L100P] leads to the development of schizophrenia-related behaviors in mice. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that interacts with the N-terminal region of DISC1 (aa 1-220) and has been implicated as an important downstream component in the etiology of schizophrenia. Here, for the first time, we show that pharmacological and genetic inactivation of GSK-3 reverse prepulse inhibition and latent inhibition deficits as well as normalizing the hyperactivity of Disc1-L100P mutants. In parallel to these observations, interaction between DISC1 and GSK-3α and β is reduced in Disc1-L100P mutants. Our data provide genetic, biochemical, and behavioral evidence for a molecular link between DISC1 and GSK-3 in relation to psychopathology and highlights the value of missense mutations in dissecting the underlying and complex molecular mechanisms of neurological disorders.
2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Aubry JM, Schwald M, Ballmann E, Karege F. Early effects of mood stabilizers on the Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway and on cell survival and proliferation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2009;205:419–429. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG. Akt/GSK-3 signaling in the action of psychotropic drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009;49:327–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
