Expression and function of ATIP/MTUS1 in human prostate cancer cell lines
- PMID: 20687230
- PMCID: PMC6528809
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.21192
Expression and function of ATIP/MTUS1 in human prostate cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: We have previously demonstrated Ang II type 2 (AT(2)-) receptor-mediated inhibition of EGF-induced prostate cancer cell growth in androgen-dependent (LNCaP) and independent (PC3) prostate cancer cell lines.
Methods: To explore the signaling pathways involved in this inhibitory effect, we examined the interaction of the AT(2)-receptor with its novel regulatory partner ATIP using real time PCR, over-expression, siRNA and [(3)H]thymidine incorporation assays.
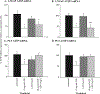
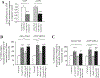
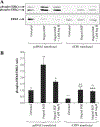
Results: The results in human prostate cancer cell lines demonstrate the presence of ATIP in both cell lines examined, and suggest that (i) the AT(2)-receptor through an interaction with ATIP mediates an anti-growth factor effect in both androgen-dependent and androgen-independent cell lines; (ii) ATIP expression decreases as the rate of cell growth and androgen-independence increase; and (iii) EGF may act on cell growth in part by reducing the content of ATIP present in the cells.
Conclusions: The results support our earlier proposal in normal cell lines that ATIP is an important component of the cellular response to AT(2)-receptor activation. The results further suggest that a critical level of ATIP is required to mediate the effect of AT(2)-receptor activation to inhibit EGF mediated increases in cell growth. They also suggest that EGF may in part induce cell growth by suppressing the level of ATIP expression.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
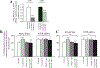
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of tumor suppressor MTUS1/ATIP is associated with enhanced proliferation, poor differentiation and poor prognosis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Oncol. 2012 Feb;6(1):73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Mol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22153618 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of MTUS1/ATIP and Its Major Isoforms, ATIP1 and ATIP3, in Human Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Oct 11;3(4):3824-37. doi: 10.3390/cancers3043824. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24213113 Free PMC article.
-
Functional angiotensin II type 2 receptors inhibit growth factor signaling in LNCaP and PC3 prostate cancer cell lines.Prostate. 2008 May 1;68(6):651-60. doi: 10.1002/pros.20738. Prostate. 2008. PMID: 18288685
-
Increased expression of heparin binding EGF (HB-EGF), amphiregulin, TGF alpha and epiregulin in androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines.Anticancer Res. 2000 Jan-Feb;20(1A):91-5. Anticancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10769639
-
Mutation analysis of the 8p22 candidate tumor suppressor gene ATIP/MTUS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006 Jun 27;252(1-2):207-15. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.014. Epub 2006 May 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16650523 Review.
Cited by
-
ATIP/ATIP1 regulates prostate cancer metastasis through mitochondrial dynamic-dependent signaling.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Feb 25;56(2):304-314. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024006. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38282475 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of tumor suppressor MTUS1/ATIP is associated with enhanced proliferation, poor differentiation and poor prognosis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Oncol. 2012 Feb;6(1):73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Mol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22153618 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA PRR7-AS1 promotes osteosarcoma progression via binding RNF2 to transcriptionally suppress MTUS1.Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 16;13:1227789. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1227789. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38033505 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule associated tumor suppressor 1 deficient mice develop spontaneous heart hypertrophy and SLE-like lymphoproliferative disease.Int J Oncol. 2012 Apr;40(4):1079-88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1311. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22200760 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of MTUS1/ATIP and Its Major Isoforms, ATIP1 and ATIP3, in Human Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Oct 11;3(4):3824-37. doi: 10.3390/cancers3043824. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24213113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abali H, Gullu I, Engin H, Haznedaroglu I, Erman M, Tekuzman G. Old antihypertensives as novel antineoplastics: Angiotensin- I-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Med Hypotheses 2002;59:344–348. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto Y, Sasaki T, Tsuchida A, Chayama K. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in human pancreatic cancer and growth inhibition by angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist. FEBS Lett 2001;495:197–200. - PubMed
-
- Fujita M, Hayashi I, Yamashina S, Itoman M, Majima M. Blockade of angiotensin AT1a receptor signaling reduces tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;294:441–447. - PubMed
-
- Lever AF, Hole DJ, Gillis CR, McCallum IR, McInnes GT, MacKinnon PL, Meredith PA, Murray LS, Reid JL, Robertson JW. Do inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme protect against risk of cancer? Lancet 1998;352:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Kawata M, Yoshii J, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R, Nakatani T, Tsujinoue H, Fukui H. The angiotensin-I- converting enzyme inhibitor perindopril suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis: Possible role of the vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 2001;7:1073–1078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

