Role of small RNAs in host-microbe interactions
- PMID: 20687832
- PMCID: PMC3752435
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-073009-114457
Role of small RNAs in host-microbe interactions
Abstract
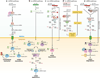
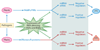
Plant defense responses against pathogens are mediated by activation and repression of a large array of genes. Host endogenous small RNAs are essential in this gene expression reprogramming process. Here, we discuss recent findings on pathogen-regulated host microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and their roles in plant-microbe interaction. We further introduce small RNA pathway components, including Dicer-like proteins (DCLs), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) binding protein, RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RDRs), small RNA methyltransferase HEN1, and Argonaute (AGO) proteins, that contribute to plant immune responses. The strategies that pathogens have evolved to suppress host small RNA pathways are also discussed. Collectively, host small RNAs and RNA silencing machinery constitute a critical layer of defense in regulating the interaction of pathogens with plants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Host small RNAs are big contributors to plant innate immunity.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009 Aug;12(4):465-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2009.06.005. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009. PMID: 19608454 Review.
-
Contribution of small RNA pathway components in plant immunity.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Jun;26(6):617-25. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-12-0255-IA. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 23489060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Messages on small RNA duplexes in plants.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):7-16. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0876-2. Epub 2016 Nov 23. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27878651 Review.
-
Endogenous small RNAs and antibacterial immunity in plants.FEBS Lett. 2008 Aug 6;582(18):2679-84. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.053. Epub 2008 Jul 11. FEBS Lett. 2008. PMID: 18619960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA 'Information Warfare' in Pathogenic and Mutualistic Interactions.Trends Plant Sci. 2016 Sep;21(9):738-748. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Trends Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27318950 Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput sequencing of small RNA transcriptome reveals salt stress regulated microRNAs in sugarcane.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059423. Epub 2013 Mar 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23544066 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-mediated gene regulation: potential applications for plant genetic engineering.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 Sep;83(1-2):59-75. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0089-1. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23771582 Review.
-
Identification of Tomato microRNAs in Late Response to Trichoderma atroviride.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 28;25(3):1617. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031617. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338899 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of microRNAs and their targets in wild type and phyB mutant provides a key link between microRNAs and the phyB-mediated light signaling pathway in rice.Front Plant Sci. 2015 May 29;6:372. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00372. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26074936 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and profiling of small RNAs from Puccinia triticina by deep sequencing and identification of their potential targets in wheat.Funct Integr Genomics. 2019 May;19(3):391-407. doi: 10.1007/s10142-018-00652-1. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30618015
References
-
- Adenot X, Elmayan T, Lauressergues D, Boutet S, Bouché N, et al. DRB4-dependent TAS3 trans-acting siRNAs control leaf morphology through AGO7. Curr. Biol. 2006;16(9):927–932. - PubMed
-
- Anandalakshmi R, Marathe R, Ge X, Herr JM, Jr, Mau C, et al. A calmodulin-related protein that suppresses posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 2000;290:142–144. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe D. Viruses and gene silencing in plants. Arch. Virol. Suppl. 1999;15:189–201. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe D. RNA silencing in plants. Nature. 2004;431:356–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

