Vertebrate Hedgehog signaling: cilia rule
- PMID: 20687907
- PMCID: PMC2912248
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-102
Vertebrate Hedgehog signaling: cilia rule
Abstract
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway differentially utilizes the primary cilium in mammals and fruit flies. Recent work, including a study in BMC Biology, demonstrates that Hh signals through the cilium in zebrafish, clarifying the evolution of Hh signal transduction. See research article: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7007/8/65.
Figures
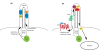
Comment on
-
Gli2a protein localization reveals a role for Iguana/DZIP1 in primary ciliogenesis and a dependence of Hedgehog signal transduction on primary cilia in the zebrafish.BMC Biol. 2010 Apr 19;8:65. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-65. BMC Biol. 2010. PMID: 20487519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aanstad P, Santos N, Corbit KC, Scherz PJ, Trinh le A, Salvenmoser W, Huisken J, Reiter JF, Stainier DY. The extracellular domain of Smoothened regulates ciliary localization and is required for high-level Hh signaling. Curr Biol. 2009;19:1034–1039. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.04.053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

