Breast tumor kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 mediate Met receptor signaling to cell migration in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20687930
- PMCID: PMC2949652
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2622
Breast tumor kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 mediate Met receptor signaling to cell migration in breast cancer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Breast tumor kinase (Brk/protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6)) is a nonreceptor, soluble tyrosine kinase overexpressed in the majority of breast tumors. Previous work has placed Brk downstream of epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB) activation and upstream of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases. Herein we investigate the regulation of Brk kinase activity and cell migration in response to treatment of keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) and breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and T47D cells) with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and macrophage stimulating protein (MSP), peptide ligands for Met and Ron receptors, respectively.
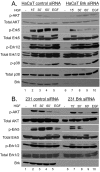
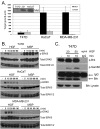
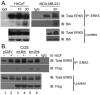
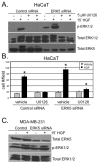
Methods: In vitro kinase assays were performed to directly measure Brk kinase activity in response to MET and RON ligands. Transfection of Brk-targeted RNAi was used to knock down endogenous Brk or ERK5 in multiple cell lines. Kinase activities (downstream of MET signaling) were assayed by Western blotting using total and phospho-specific antibodies. Boyden chamber assays were used to measure cell migration in response to manipulation of Brk and downstream MET effectors. Rescue experiments were performed by knock down of endogenous Brk using RNAi (targeting the untranslated region (3'-UTR)) and transient transfection (re-expression) of either wild-type or kinase-inactive Brk.
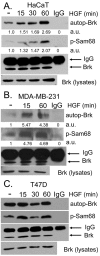
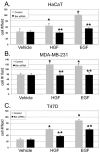
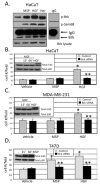
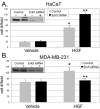
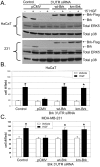
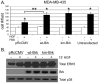
Results: Brk gene silencing revealed that HGF, but not MSP, induced robust Brk-dependent cell migration. Brk and ERK5 copurified in HGF-induced protein complexes, and Brk/ERK5 complexes formed independently of Brk kinase activity. ERK5 was required for breast cancer cell but not keratinocyte cell migration, which became ERK1/2-dependent upon ERK5 knockdown. Notably, rescue experiments indicated that the kinase activity of Brk was not required for HGF-induced cell migration. Further, expression of either wild-type or kinase-inactive Brk in Brk-null MDA-MB-435 cells activated ERK5 and conferred increased HGF-induced cell migration.
Conclusions: These results have identified Brk and ERK5 as important downstream effectors of Met signaling to cell migration. Targeting ERK5 kinase activity or inhibiting the formation of Brk/ERK5 complexes may provide an additional means of blocking cell migration associated with breast cancer progression to metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Serfas MS, Tyner AL. Brk, Srm, Frk, and Src42A form a distinct family of intracellular Src-like tyrosine kinases. Oncol Res. 2003;13:409–419. - PubMed
-
- Aubele M, Vidojkovic S, Braselmann H, Ritterswurden D, Auer G, Atkinson MJ, Tapio S, Höfler H, Rauser S, Bartlett JM. Overexpression of PTK6 (breast tumor kinase) protein--a prognostic factor for long-term breast cancer survival--is not due to gene amplification. Virchows Arch. 2009;455:117–123. doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0809-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

